+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Molecular mechanism of SbmA, a promiscuous transporter exploited by antimicrobial peptides. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Sci Adv, Vol. 7, Issue 37, Page eabj5363, Year 2021 |
| 掲載日 | 2021年9月10日 |
 著者 著者 | Dmitry Ghilarov / Satomi Inaba-Inoue / Piotr Stepien / Feng Qu / Elizabeth Michalczyk / Zuzanna Pakosz / Norimichi Nomura / Satoshi Ogasawara / Graham Charles Walker / Sylvie Rebuffat / So Iwata / Jonathan Gardiner Heddle / Konstantinos Beis /      |
| PubMed 要旨 | Antibiotic metabolites and antimicrobial peptides mediate competition between bacterial species. Many of them hijack inner and outer membrane proteins to enter cells. Sensitivity of enteric bacteria ...Antibiotic metabolites and antimicrobial peptides mediate competition between bacterial species. Many of them hijack inner and outer membrane proteins to enter cells. Sensitivity of enteric bacteria to multiple peptide antibiotics is controlled by the single inner membrane protein SbmA. To establish the molecular mechanism of peptide transport by SbmA and related BacA, we determined their cryo–electron microscopy structures at 3.2 and 6 Å local resolution, respectively. The structures show a previously unknown fold, defining a new class of secondary transporters named SbmA-like peptide transporters. The core domain includes conserved glutamates, which provide a pathway for proton translocation, powering transport. The structures show an outward-open conformation with a large cavity that can accommodate diverse substrates. We propose a molecular mechanism for antibacterial peptide uptake paving the way for creation of narrow-targeted therapeutics. |
 リンク リンク |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:34516884 / PubMed:34516884 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.59 - 6.36 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-13168: SbmA-FabS11-1 in lipid nanodisc  EMDB-13173: 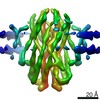 EMDB-13175: |
| 化合物 | 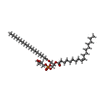 ChemComp-PGW: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / SLiPT / proton transport / peptide transport / antibiotics |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について






