+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Microtubule-binding-induced allostery triggers LIS1 dissociation from dynein prior to cargo transport. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 30, Issue 9, Page 1365-1379, Year 2023 |
| Publish date | Jun 15, 2023 |
 Authors Authors | William D Ton / Yue Wang / Pengxin Chai / Cisloynny Beauchamp-Perez / Nicholas T Flint / Lindsay G Lammers / Hao Xiong / Kai Zhang / Steven M Markus /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 ...The lissencephaly-related protein LIS1 is a critical regulator of cytoplasmic dynein that governs motor function and intracellular localization (for example, to microtubule plus-ends). Although LIS1 binding is required for dynein activity, its unbinding prior to initiation of cargo transport is equally important, since preventing dissociation leads to dynein dysfunction. To understand whether and how dynein-LIS1 binding is modulated, we engineered dynein mutants locked in a microtubule-bound (MT-B) or microtubule-unbound (MT-U) state. Whereas the MT-B mutant exhibits low LIS1 affinity, the MT-U mutant binds LIS1 with high affinity, and as a consequence remains almost irreversibly associated with microtubule plus-ends. We find that a monomeric motor domain is sufficient to exhibit these opposing LIS1 affinities, and that this is evolutionarily conserved between yeast and humans. Three cryo-EM structures of human dynein with and without LIS1 reveal microtubule-binding induced conformational changes responsible for this regulation. Our work reveals key biochemical and structural insight into LIS1-mediated dynein activation. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:37322240 / PubMed:37322240 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.9 - 3.4 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-28999, PDB-8fcy: EMDB-29003, PDB-8fd6: EMDB-29012, PDB-8fdt: EMDB-29014, PDB-8fdu: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-ATP: 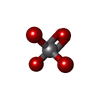 ChemComp-VO4:  ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / Dynein / motor domain / microtubule-bound / microtubule-unbound / LIS1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers








 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
 thermus thermophilus (bacteria)
thermus thermophilus (bacteria)