+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural transitions of F-actin upon ATP hydrolysis at near-atomic resolution revealed by cryo-EM. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Struct Mol Biol, Vol. 25, Issue 6, Page 528-537, Year 2018 |
| Publish date | Jun 4, 2018 |
 Authors Authors | Felipe Merino / Sabrina Pospich / Johanna Funk / Thorsten Wagner / Florian Küllmer / Hans-Dieter Arndt / Peter Bieling / Stefan Raunser /  |
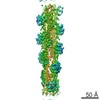
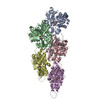
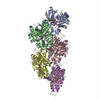
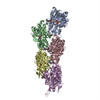
| PubMed Abstract | The function of actin is coupled to the nucleotide bound to its active site. ATP hydrolysis is activated during polymerization; a delay between hydrolysis and inorganic phosphate (P) release results ...The function of actin is coupled to the nucleotide bound to its active site. ATP hydrolysis is activated during polymerization; a delay between hydrolysis and inorganic phosphate (P) release results in a gradient of ATP, ADP-P and ADP along actin filaments (F-actin). Actin-binding proteins can recognize F-actin's nucleotide state, using it as a local 'age' tag. The underlying mechanism is complex and poorly understood. Here we report six high-resolution cryo-EM structures of F-actin from rabbit skeletal muscle in different nucleotide states. The structures reveal that actin polymerization repositions the proposed catalytic base, His161, closer to the γ-phosphate. Nucleotide hydrolysis and P release modulate the conformational ensemble at the periphery of the filament, thus resulting in open and closed states, which can be sensed by coronin-1B. The drug-like toxin jasplakinolide locks F-actin in an open state. Our results demonstrate in detail how ATP hydrolysis links to F-actin's conformational dynamics and protein interaction. |
 External links External links |  Nat Struct Mol Biol / Nat Struct Mol Biol /  PubMed:29867215 PubMed:29867215 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.3 - 4.1 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-3835, PDB-5onv: EMDB-3836, PDB-5ooc: EMDB-3837, PDB-5ood: EMDB-3838, PDB-5ooe: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-9ZK:  ChemComp-PO4:  ChemComp-ANP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Cytoskeleton / nucleotide states / filament stability / cell migration |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers