+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure and conformational variability of the mycobacterium tuberculosis fatty acid synthase multienzyme complex. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Structure, Vol. 21, Issue 7, Page 1251-1257, Year 2013 |
| Publish date | Jul 2, 2013 |
 Authors Authors | Luciano Ciccarelli / Sean R Connell / Mathias Enderle / Deryck J Mills / Janet Vonck / Martin Grininger /  |
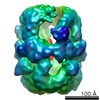
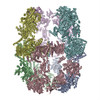
| PubMed Abstract | Antibiotic therapy in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections targets de novo fatty acid biosynthesis, which is orchestrated by a 1.9 MDa type I fatty acid synthase (FAS). Here, we ...Antibiotic therapy in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections targets de novo fatty acid biosynthesis, which is orchestrated by a 1.9 MDa type I fatty acid synthase (FAS). Here, we characterize M. tuberculosis FAS by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy and interpret the data by docking the molecular models of yeast and Mycobacterium smegmatis FAS. Our analysis reveals a porous barrel-like structure of considerable conformational variability that is illustrated by the identification of several conformational states with altered topology in the multienzymatic assembly. This demonstrates that the barrel-like structure of M. tuberculosis FAS is not just a static scaffold for the catalytic domains, but may play an active role in coordinating fatty acid synthesis. The conception of M. tuberculosis FAS as a highly dynamic assembly of domains revises the view on bacterial type I fatty acid synthesis and might inspire new strategies for inhibition of de novo fatty acid synthesis in M. tuberculosis. |
 External links External links |  Structure / Structure /  PubMed:23746808 PubMed:23746808 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 17.5 - 27.0 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-2357, PDB-4v8w: EMDB-2358, PDB-4v8v: 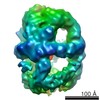 EMDB-2359: |
| Chemicals | 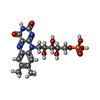 ChemComp-FMN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / CODIMENSIONAL PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS / FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS / SAMPLE HETEROGENEITY / PROTEIN FLEXIBILITY |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers