+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | The presence and absence of periplasmic rings in bacterial flagellar motors correlates with stator type. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Elife, Vol. 8, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Jan 16, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Mohammed Kaplan / Debnath Ghosal / Poorna Subramanian / Catherine M Oikonomou / Andreas Kjaer / Sahand Pirbadian / Davi R Ortega / Ariane Briegel / Mohamed Y El-Naggar / Grant J Jensen /  |
| PubMed Abstract | The bacterial flagellar motor, a cell-envelope-embedded macromolecular machine that functions as a cellular propeller, exhibits significant structural variability between species. Different torque- ...The bacterial flagellar motor, a cell-envelope-embedded macromolecular machine that functions as a cellular propeller, exhibits significant structural variability between species. Different torque-generating stator modules allow motors to operate in different pH, salt or viscosity levels. How such diversity evolved is unknown. Here, we use electron cryo-tomography to determine the in situ macromolecular structures of three Gammaproteobacteria motors: , , and , providing the first views of intact motors with dual stator systems. Complementing our imaging with bioinformatics analysis, we find a correlation between the motor's stator system and its structural elaboration. Motors with a single H-driven stator have only the core periplasmic P- and L-rings; those with dual H-driven stators have an elaborated P-ring; and motors with Na or Na/H-driven stators have both their P- and L-rings embellished. Our results suggest an evolution of structural elaboration that may have enabled pathogenic bacteria to colonize higher-viscosity environments in animal hosts. |
 External links External links |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:30648971 / PubMed:30648971 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (subtomogram averaging) |
| Resolution | 59.0 - 69.0 Å |
| Structure data | 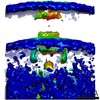 EMDB-0464:  EMDB-0465: 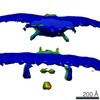 EMDB-0467: |
| Source |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




