+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Two solutions for efficient light-harvesting in phototrophic . |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | mSystems, Vol. 11, Issue 1, Page e0109425, Year 2026 |
| Publish date | Jan 20, 2026 |
 Authors Authors | Alastair T Gardiner / Yibo Jin / David Bína / Maarten Joosten / David Kaftan / Izabela Mujakić / Zdenko Gardian / Pablo Castro-Hartmann / Pu Qian / Michal Koblížek /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Phototrophic Gemmatimonadota represent a unique group of phototrophic bacteria that acquired a complete set of photosynthetic genes via horizontal gene transfer and later evolved independently. () ...Phototrophic Gemmatimonadota represent a unique group of phototrophic bacteria that acquired a complete set of photosynthetic genes via horizontal gene transfer and later evolved independently. () contains photosynthetic complexes with two concentric light-harvesting antenna rings that absorb at 816 and 868 nm, allowing it to better exploit the light conditions found deeper in the water column. The closely related species , with highly similar photosynthetic genes, harvests infrared light using a single 860 nm absorption band. The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the photosynthetic complex reveals that the outer antenna lacks monomeric bacteriochlorophylls, resulting in a smaller optical antenna cross-section. The spectrum is red-shifted relative to due to the formation of a H-bond enabled by a different rotamer conformation of αTrp in the outer ring. This H-bond forms with a neighboring bacteriochlorophyll and increases the intra-dimer exciton coupling, affecting the exciton localization probability within the rings and increasing exciton cooperativity between the complexes. The functional consequences of the spectral shift, caused solely by a subtle conformational change of a single residue, represent a novel mechanism in which phototrophic organisms adjust their antennae for particular light conditions and enable to grow higher in the water column where more photons are available.IMPORTANCEThe photoheterotrophic species of the phylum Gemmatimonadota employ unique photosynthetic complexes with two concentric antenna rings around a central reaction center. In contrast to other phototrophic species, these organisms have not evolved any regulatory systems to control the expression of their photosynthetic apparatus under different light conditions. Despite the overall similarity, the complexes present in and have different absorption properties in the near-infrared region of the spectrum that make them more suitable for low or medium light, respectively. The main difference in absorption depends on the conformation of a single tryptophan residue that can form an H-bond with a neighboring bacteriochlorophyll. The presence or absence of this H-bond affects how the protein scaffold interacts with the bacteriochlorophylls, which in turn determines how light energy is transferred within and between the photosynthetic complexes. |
 External links External links |  mSystems / mSystems /  PubMed:41342568 / PubMed:41342568 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.3 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-51788, PDB-9h22: |
| Chemicals | 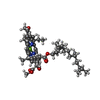 ChemComp-BCL: 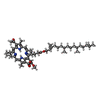 ChemComp-BPH: 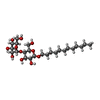 ChemComp-LMT:  ChemComp-MQ8:  ChemComp-FE:  ChemComp-CD4:  ChemComp-CRT:  ChemComp-PEX:  ChemComp-HEC:  ChemComp-V7N:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / photosynthetic bacteria / reaction cennter light harvesting complex / RC-LH1 / RC-dLH / cryo-EM / Gemmatimonas groenlandica |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 gemmatimonas groenlandica (bacteria)
gemmatimonas groenlandica (bacteria)