+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Platelet integrin αIIbβ3 plays a key role in a venous thrombogenesis mouse model. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 15, Issue 1, Page 8612, Year 2024 |
| 掲載日 | 2024年10月4日 |
 著者 著者 | Brian D Adair / Conroy O Field / José L Alonso / Jian-Ping Xiong / Shi-Xian Deng / Hyun Sook Ahn / Eivgeni Mashin / Clary B Clish / Johannes van Agthoven / Mark Yeager / Youzhong Guo / David A Tess / Donald W Landry / Mortimer Poncz / M Amin Arnaout /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Venous thrombosis (VT) is a common vascular disease associated with reduced survival and a high recurrence rate. VT is initiated by the accumulation of platelets and neutrophils at sites of ...Venous thrombosis (VT) is a common vascular disease associated with reduced survival and a high recurrence rate. VT is initiated by the accumulation of platelets and neutrophils at sites of endothelial cell activation. A role for platelet αIIbβ3 in VT is not established, a task complicated by the increased bleeding risk caused by partial agonists such as tirofiban. Here, we show that m-tirofiban, a modified version of tirofiban, does not agonize αIIbβ3 based on lack of neoepitope expression and the cryo-EM structure of m-tirofiban/full-length αIIbβ3 complex. m-tirofiban abolishes agonist-induced platelet aggregation while preserving clot retraction ex vivo and, unlike tirofiban, it suppresses venous thrombogenesis in a mouse model without increasing bleeding. These findings establish a key role for αIIbβ3 in VT initiation and suggest that m-tirofiban and compounds with a similar structurally-defined mechanism of action merit consideration as potential thromboprophylaxis agents in patients at high risk for VT and hemorrhage. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:39366965 / PubMed:39366965 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 3.9 - 4.1 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-46793, PDB-9deq: EMDB-46794, PDB-9der: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-MG: 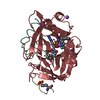 PDB-1a5g:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-HOH: 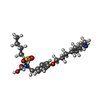 ChemComp-AGG: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | CELL ADHESION / complex / open headpiece |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について







 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)