+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Ball-and-chain inactivation in a calcium-gated potassium channel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 580, Issue 7802, Page 288-293, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Mar 18, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Chen Fan / Nattakan Sukomon / Emelie Flood / Jan Rheinberger / Toby W Allen / Crina M Nimigean /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Inactivation is the process by which ion channels terminate ion flux through their pores while the opening stimulus is still present. In neurons, inactivation of both sodium and potassium channels is ...Inactivation is the process by which ion channels terminate ion flux through their pores while the opening stimulus is still present. In neurons, inactivation of both sodium and potassium channels is crucial for the generation of action potentials and regulation of firing frequency. A cytoplasmic domain of either the channel or an accessory subunit is thought to plug the open pore to inactivate the channel via a 'ball-and-chain' mechanism. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to identify the molecular gating mechanism in calcium-activated potassium channels by obtaining structures of the MthK channel from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum-a purely calcium-gated and inactivating channel-in a lipid environment. In the absence of Ca, we obtained a single structure in a closed state, which was shown by atomistic simulations to be highly flexible in lipid bilayers at ambient temperature, with large rocking motions of the gating ring and bending of pore-lining helices. In Ca-bound conditions, we obtained several structures, including multiple open-inactivated conformations, further indication of a highly dynamic protein. These different channel conformations are distinguished by rocking of the gating rings with respect to the transmembrane region, indicating symmetry breakage across the channel. Furthermore, in all conformations displaying open channel pores, the N terminus of one subunit of the channel tetramer sticks into the pore and plugs it, with free energy simulations showing that this is a strong interaction. Deletion of this N terminus leads to functionally non-inactivating channels and structures of open states without a pore plug, indicating that this previously unresolved N-terminal peptide is responsible for a ball-and-chain inactivation mechanism. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:32269335 / PubMed:32269335 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 6.7 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-20650, PDB-6u5n: EMDB-20652, PDB-6u5p: EMDB-20653, PDB-6u5r: EMDB-20662, PDB-6u68: EMDB-20663, PDB-6u6d: EMDB-20664, PDB-6u6e: EMDB-20665, PDB-6u6h: EMDB-20925, PDB-6uwn: EMDB-20929, PDB-6ux4: EMDB-20930, PDB-6ux7: EMDB-20931, PDB-6uxa: EMDB-20932, PDB-6uxb: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-K: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / MthK / inactivation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





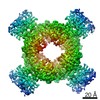

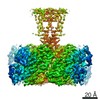
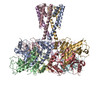
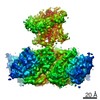
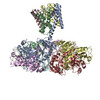
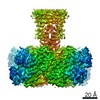
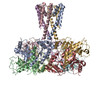
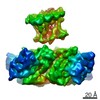




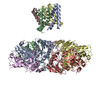
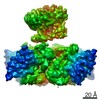
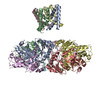
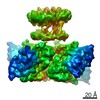

 methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea)
methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (archaea)