+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Dimeric structures of quinol-dependent nitric oxide reductases (qNORs) revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Sci Adv, Vol. 5, Issue 8, Page eaax1803, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Aug 28, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Chai C Gopalasingam / Rachel M Johnson / George N Chiduza / Takehiko Tosha / Masaki Yamamoto / Yoshitsugu Shiro / Svetlana V Antonyuk / Stephen P Muench / S Samar Hasnain /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Quinol-dependent nitric oxide reductases (qNORs) are membrane-integrated, iron-containing enzymes of the denitrification pathway, which catalyze the reduction of nitric oxide (NO) to the major ozone ...Quinol-dependent nitric oxide reductases (qNORs) are membrane-integrated, iron-containing enzymes of the denitrification pathway, which catalyze the reduction of nitric oxide (NO) to the major ozone destroying gas nitrous oxide (NO). Cryo-electron microscopy structures of active qNOR from and an activity-enhancing mutant have been determined to be at local resolutions of 3.7 and 3.2 Å, respectively. They unexpectedly reveal a dimeric conformation (also confirmed for qNOR from ) and define the active-site configuration, with a clear water channel from the cytoplasm. Structure-based mutagenesis has identified key residues involved in proton transport and substrate delivery to the active site of qNORs. The proton supply direction differs from cytochrome c-dependent NOR (cNOR), where water molecules from the cytoplasm serve as a proton source similar to those from cytochrome c oxidase. |
 External links External links |  Sci Adv / Sci Adv /  PubMed:31489376 / PubMed:31489376 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.3 - 3.9 Å |
| Structure data | |
| Chemicals | 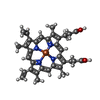 ChemComp-HEM:  ChemComp-FE:  ChemComp-CA: 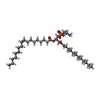 ChemComp-LOP: 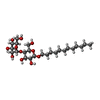 ChemComp-LMT:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / Proton Transfer / Membrane Protein / Homodimer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers





 Achromobacter xylosoxidans (bacteria)
Achromobacter xylosoxidans (bacteria)