+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Catastrophic disassembly of actin filaments via Mical-mediated oxidation. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Nat Commun, Vol. 8, Issue 1, Page 2183, Year 2017 |
| 掲載日 | 2017年12月19日 |
 著者 著者 | Elena E Grintsevich / Peng Ge / Michael R Sawaya / Hunkar Gizem Yesilyurt / Jonathan R Terman / Z Hong Zhou / Emil Reisler /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | Actin filament assembly and disassembly are vital for cell functions. MICAL Redox enzymes are important post-translational effectors of actin that stereo-specifically oxidize actin's M44 and M47 ...Actin filament assembly and disassembly are vital for cell functions. MICAL Redox enzymes are important post-translational effectors of actin that stereo-specifically oxidize actin's M44 and M47 residues to induce cellular F-actin disassembly. Here we show that Mical-oxidized (Mox) actin can undergo extremely fast (84 subunits/s) disassembly, which depends on F-actin's nucleotide-bound state. Using near-atomic resolution cryoEM reconstruction and single filament TIRF microscopy we identify two dynamic and structural states of Mox-actin. Modeling actin's D-loop region based on our 3.9 Å cryoEM reconstruction suggests that oxidation by Mical reorients the side chain of M44 and induces a new intermolecular interaction of actin residue M47 (M47-O-T351). Site-directed mutagenesis reveals that this interaction promotes Mox-actin instability. Moreover, we find that Mical oxidation of actin allows for cofilin-mediated severing even in the presence of inorganic phosphate. Thus, in conjunction with cofilin, Mical oxidation of actin promotes F-actin disassembly independent of the nucleotide-bound state. |
 リンク リンク |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:29259197 / PubMed:29259197 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
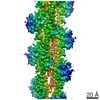
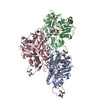
| 手法 | EM (らせん対称) / X線回折 |
| 解像度 | 2.39 - 3.9 Å |
| 構造データ | 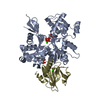 PDB-5ubo: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-CA:  ChemComp-ATP: 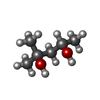 ChemComp-MPD:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | CONTRACTILE PROTEIN / GELSOLIN / ACTIN / METHIONINE OXIDATION / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / F-Actin / Mical / cytoskeleton / helix |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について




 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)