+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | X-ray and cryo-EM structures of monomeric and filamentous actin-like protein MamK reveal changes associated with polymerization. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 113, Issue 47, Page 13396-13401, Year 2016 |
| Publish date | Nov 22, 2016 |
 Authors Authors | Jan Löwe / Shaoda He / Sjors H W Scheres / Christos G Savva /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Magnetotactic bacteria produce iron-rich magnetic nanoparticles that are enclosed by membrane invaginations to form magnetosomes so they are able to sense and act upon Earth's magnetic field. In ...Magnetotactic bacteria produce iron-rich magnetic nanoparticles that are enclosed by membrane invaginations to form magnetosomes so they are able to sense and act upon Earth's magnetic field. In Magnetospirillum and other magnetotactic bacteria, to combine their magnetic moments, magnetosomes align along filaments formed by a bacterial actin homolog, MamK. Here, we present the crystal structure of a nonpolymerizing mutant of MamK from Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 at 1.8-Å resolution, revealing its close similarity to actin and MreB. The crystals contain AMPPNP-bound monomeric MamK in two different conformations. To investigate conformational changes associated with polymerization, we used unmodified MamK protein and cryo-EM with helical 3D reconstruction in RELION to obtain a density map and a fully refined atomic model of MamK in filamentous form at 3.6-Å resolution. The filament is parallel (polar) double-helical, with a rise of 52.2 Å and a twist of 23.8°. As shown previously and unusually for actin-like filaments, the MamK subunits from each of the two strands are juxtaposed, creating an additional twofold axis along the filament. Compared with monomeric MamK, ADP-bound MamK in the filament undergoes a conformational change, rotating domains I and II against each other to further close the interdomain cleft between subdomains IB and IIB. The domain movement causes several loops to close around the nucleotide-binding pocket. Glu-143, a key residue for catalysis coordinating the magnesium ion, moves closer, presumably switching nucleotide hydrolysis upon polymerization-one of the hallmarks of cytomotive filaments of the actin type. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:27821762 / PubMed:27821762 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (helical sym.) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.8 - 3.64 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-4062: MamK double helical filament at 3.6 A resolution 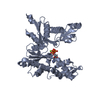 PDB-5ljw: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-ANP:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  bacterial cytoskeleton / bacterial cytoskeleton /  filamentous protein / filamentous protein /  actin-like / magnetosomes / actin-like / magnetosomes /  HYDROLASE HYDROLASE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 magnetospirillum magneticum amb-1 (bacteria)
magnetospirillum magneticum amb-1 (bacteria)