+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 527, Issue 7576, Page 64-69, Year 2015 |
| Publish date | Nov 5, 2015 |
 Authors Authors | Jingpeng Ge / Wanqiu Li / Qiancheng Zhao / Ningning Li / Maofei Chen / Peng Zhi / Ruochong Li / Ning Gao / Bailong Xiao / Maojun Yang /  |
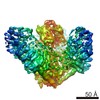
| PubMed Abstract | Piezo proteins are evolutionarily conserved and functionally diverse mechanosensitive cation channels. However, the overall structural architecture and gating mechanisms of Piezo channels have ...Piezo proteins are evolutionarily conserved and functionally diverse mechanosensitive cation channels. However, the overall structural architecture and gating mechanisms of Piezo channels have remained unknown. Here we determine the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the full-length (2,547 amino acids) mouse Piezo1 (Piezo1) at a resolution of 4.8 Å. Piezo1 forms a trimeric propeller-like structure (about 900 kilodalton), with the extracellular domains resembling three distal blades and a central cap. The transmembrane region has 14 apparently resolved segments per subunit. These segments form three peripheral wings and a central pore module that encloses a potential ion-conducting pore. The rather flexible extracellular blade domains are connected to the central intracellular domain by three long beam-like structures. This trimeric architecture suggests that Piezo1 may use its peripheral regions as force sensors to gate the central ion-conducting pore. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:26390154 PubMed:26390154 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.45 - 4.8 Å |
| Structure data |  PDB-4rax: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | METAL TRANSPORT / Cryo-EM / single particle / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / sandwich fold / novel structure / extra-cellular / regulatory domain / regulatory |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers