+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Mechanism of cotranslational protein N-myristoylation in human cells. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Mol Cell, Vol. 85, Issue 14, Page 2749-22758.e8, Year 2025 |
| 掲載日 | 2025年7月17日 |
 著者 著者 | Martin Gamerdinger / Blanca Echeverria / Alfred M Lentzsch / Nicolas Burg / Ziyi Fan / Mateusz Jaskolowski / Alain Scaiola / Selina Piening / Shu-Ou Shan / Nenad Ban / Elke Deuerling /    |
| PubMed 要旨 | N-myristoyltransferases (NMTs) cotranslationally transfer the fatty acid myristic acid to the N terminus of newly synthesized proteins, regulating their function and cellular localization. These ...N-myristoyltransferases (NMTs) cotranslationally transfer the fatty acid myristic acid to the N terminus of newly synthesized proteins, regulating their function and cellular localization. These enzymes are important drug targets for the treatment of cancer and viral infections. N-myristoylation of nascent proteins occurs specifically on N-terminal glycine residues after the excision of the initiator methionine by methionine aminopeptidases (METAPs). How NMTs interact with ribosomes and gain timely and specific access to their substrates remains unknown. Here, we show that human NMT1 exchanges with METAP1 at the ribosomal tunnel exit to form an active cotranslational complex together with the nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC). NMT1 binding is sequence selective and specifically triggered by methionine excision, which exposes the N-myristoylation motif in the nascent chain. The revealed mode of interaction of NMT1 with NAC and the methionine-cleaved nascent protein elucidates how a specific subset of proteins can be efficiently N-myristoylated in human cells. |
 リンク リンク |  Mol Cell / Mol Cell /  PubMed:40639378 PubMed:40639378 |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.8 - 3.43 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-53295, PDB-9qqa: EMDB-53296, PDB-9qqb: |
| 化合物 |  ChemComp-MG: 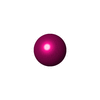 ChemComp-UNX: 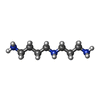 ChemComp-SPD: 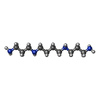 ChemComp-SPM:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-IHP: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | RIBOSOME / Translation / co-translational protein processing |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア EMN文献について
EMN文献について








 homo sapiens (ヒト)
homo sapiens (ヒト)