[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8150: Structure and dynamics of single-isoform recombinant neuronal hum... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8150 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure and dynamics of single-isoform recombinant neuronal human tubulin | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | None | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | microtubules / tubulin / single isoform / recombinant / dynamic instability / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnetrin receptor binding / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / axonemal microtubule / dorsal root ganglion development / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / organelle transport along microtubule / glial cell differentiation / forebrain morphogenesis ...netrin receptor binding / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / axonemal microtubule / dorsal root ganglion development / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / organelle transport along microtubule / glial cell differentiation / forebrain morphogenesis / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / neuron projection arborization / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / cerebellar cortex morphogenesis / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / dentate gyrus development / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / pyramidal neuron differentiation / Gap junction assembly / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / Kinesins / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / centrosome cycle / motor behavior / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / response to L-glutamate / smoothened signaling pathway / intercellular bridge / regulation of synapse organization / startle response / locomotory exploration behavior / Recycling pathway of L1 / microtubule polymerization / microtubule-based process / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / response to tumor necrosis factor / Hedgehog 'off' state / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / response to mechanical stimulus / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / condensed chromosome / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / MHC class II antigen presentation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / cellular response to calcium ion / adult locomotory behavior / filopodium / axon guidance / cell periphery / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / intracellular protein transport / neuron migration / peptide binding / synapse organization / neuromuscular junction / visual learning / PKR-mediated signaling / recycling endosome / cerebral cortex development / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / mitotic spindle / memory / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Aggrephagy / HCMV Early Events / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / Separation of Sister Chromatids / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / microtubule cytoskeleton / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / lamellipodium / mitotic cell cycle / gene expression / growth cone / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / neuron apoptotic process / microtubule / hydrolase activity / protein heterodimerization activity / cell division / axon / GTPase activity / neuronal cell body / dendrite / protein-containing complex binding / GTP binding / structural molecule activity / extracellular exosome / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.0 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Vemu A / Atherton J | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2016 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2016Title: Structure and Dynamics of Single-isoform Recombinant Neuronal Human Tubulin. Authors: Annapurna Vemu / Joseph Atherton / Jeffrey O Spector / Agnieszka Szyk / Carolyn A Moores / Antonina Roll-Mecak /   Abstract: Microtubules are polymers that cycle stochastically between polymerization and depolymerization, i.e. they exhibit "dynamic instability." This behavior is crucial for cell division, motility, and ...Microtubules are polymers that cycle stochastically between polymerization and depolymerization, i.e. they exhibit "dynamic instability." This behavior is crucial for cell division, motility, and differentiation. Although studies in the last decade have made fundamental breakthroughs in our understanding of how cellular effectors modulate microtubule dynamics, analysis of the relationship between tubulin sequence, structure, and dynamics has been held back by a lack of dynamics measurements with and structural characterization of homogeneous isotypically pure engineered tubulin. Here, we report for the first time the cryo-EM structure and in vitro dynamics parameters of recombinant isotypically pure human tubulin. α1A/βIII is a purely neuronal tubulin isoform. The 4.2-Å structure of post-translationally unmodified human α1A/βIII microtubules shows overall similarity to that of heterogeneous brain microtubules, but it is distinguished by subtle differences at polymerization interfaces, which are hot spots for sequence divergence between tubulin isoforms. In vitro dynamics assays show that, like mosaic brain microtubules, recombinant homogeneous microtubules undergo dynamic instability, but they polymerize slower and have fewer catastrophes. Interestingly, we find that epitaxial growth of α1A/βIII microtubules from heterogeneous brain seeds is inefficient but can be fully rescued by incorporating as little as 5% of brain tubulin into the homogeneous α1A/βIII lattice. Our study establishes a system to examine the structure and dynamics of mammalian microtubules with well defined tubulin species and is a first and necessary step toward uncovering how tubulin genetic and chemical diversity is exploited to modulate intrinsic microtubule dynamics. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8150.map.gz emd_8150.map.gz | 1.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8150-v30.xml emd-8150-v30.xml emd-8150.xml emd-8150.xml | 13 KB 13 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8150.png emd_8150.png | 234.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8150.cif.gz emd-8150.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8150 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8150 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8150 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8150 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_8150_validation.pdf.gz emd_8150_validation.pdf.gz | 426.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_8150_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_8150_full_validation.pdf.gz | 425.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_8150_validation.xml.gz emd_8150_validation.xml.gz | 4.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_8150_validation.cif.gz emd_8150_validation.cif.gz | 4.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8150 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8150 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8150 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8150 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5jcoMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10071 (Title: Structure and Dynamics of Single-isoform Recombinant Neuronal Human Tubulin EMPIAR-10071 (Title: Structure and Dynamics of Single-isoform Recombinant Neuronal Human TubulinData size: 487.7 Data #1: Unaligned frame stacks of GMPCPP-bound alpha1a beta3 recombinant tubulin microtubules [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8150.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 10.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8150.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 10.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.22 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Microtubules
| Entire | Name: Microtubules |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Microtubules
| Supramolecule | Name: Microtubules / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: 14pf GMPCPP-bound microtubule composed of human beta3 and alpha1a tubulin |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 110 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin beta-3 chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta-3 chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.809926 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPSGNYVGDS DLQLERISVY YNEASSHKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGA FGHLFRPDN FIFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKECENCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKVREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPSGNYVGDS DLQLERISVY YNEASSHKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGA FGHLFRPDN FIFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKECENCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKVREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS IHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLA TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT SL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTARG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVATVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLAIQSK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKVAVCDI PPRGLKMSST FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY Q UniProtKB: Tubulin beta-3 chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1A chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1A chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.649023 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLIGQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRIHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRTIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YQPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GV UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1A chain |
-Macromolecule #3: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: G2P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 521.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 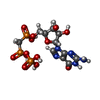 ChemComp-G2P: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.9 / Component - Name: BRB80 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-20 (5k x 3k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δz: 8.86 Å Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Δ&Phi: -25.71 ° Applied symmetry - Helical parameters - Axial symmetry: C14 (14 fold cyclic) Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER Details: Overall map resolution was 4.2 Angstrom by gold-standard FSCtrue (Chen et al., 2013). The tubulin portion of the map was at higher resolution: at least 4 Angstrom according to the Blocres resolution measure. Number images used: 10164 |
|---|---|
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: Synthetic Kinesin Decorated Microtubule |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















