[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-60885: Chloroflexus aurantiacus ADP-bound ATP synthase, state 3, focused... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Chloroflexus aurantiacus ADP-bound ATP synthase, state 3, focused refinement of FO and peripheral stalk | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ATP synthesis / proton channels / proton-motive force / proton translocation / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / : / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / lipid binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.18 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang X / Wu J / Xu X | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: Structure of ATP synthase from an early photosynthetic bacterium . Authors: Xin Zhang / Jingyi Wu / Zhenzhen Min / Jiamao Wang / Xin Hong / Xinkai Pei / Zihe Rao / Xiaoling Xu /  Abstract: F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic ...F-type ATP synthase (FF) catalyzes proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria. Different from the mitochondrial and bacterial enzymes, FF from photosynthetic organisms have evolved diverse structural and mechanistic details to adapt to the light-dependent reactions. Although complete structure of chloroplast FF has been reported, no high-resolution structure of an FF from photosynthetic bacteria has been available. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of an intact and functionally competent FF from (FF), a filamentous anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from the earliest branch of photosynthetic organisms. The structures of FF in its ADP-free and ADP-bound forms for three rotational states reveal a previously unrecognized architecture of ATP synthases. A pair of peripheral stalks connect to the F head through a dimer of δ-subunits, and associate with two membrane-embedded a-subunits that are asymmetrically positioned outside and clamp F's c-ring. The two a-subunits constitute two proton inlets on the periplasmic side and two proton outlets on the cytoplasmic side, endowing FF with unique proton translocation pathways that allow more protons being translocated relative to single a-subunit FF. Our findings deepen understanding of the architecture and proton translocation mechanisms of FF synthases and suggest innovative strategies for modulating their activities by altering the number of a-subunit. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_60885.map.gz emd_60885.map.gz | 120.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-60885-v30.xml emd-60885-v30.xml emd-60885.xml emd-60885.xml | 18.1 KB 18.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_60885_fsc.xml emd_60885_fsc.xml | 13.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_60885.png emd_60885.png | 43.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-60885.cif.gz emd-60885.cif.gz | 5.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_60885_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60885_half_map_1.map.gz emd_60885_half_map_2.map.gz emd_60885_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.5 MB 226.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60885 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60885 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60885 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-60885 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_60885_validation.pdf.gz emd_60885_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_60885_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_60885_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_60885_validation.xml.gz emd_60885_validation.xml.gz | 22.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_60885_validation.cif.gz emd_60885_validation.cif.gz | 28.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60885 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60885 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60885 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-60885 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9iu0MC  9itjC  9itkC  9itlC  9itmC  9itnC  9itoC  9itpC  9itqC  9itrC  9itsC  9ittC  9ituC  9itvC  9itwC  9itxC  9ityC  9itzC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_60885.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_60885.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.93 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
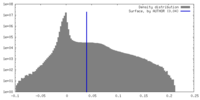
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_60885_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_60885_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ATP synthase
| Entire | Name: ATP synthase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ATP synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: ATP synthase / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: ATP synthase subunit b
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase subunit b / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.710455 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MEALGINPTL FIAQLINFLL LIFILRALLY RPVMNLLNER TRRIEESVRD AEKVREQLAN ARRDYEAEIA RARQEAAKIV AQAQERAKQ QEAEIIAQAR REAERLKEEA RAQAEQERIR MLSEAKSQIA DLVTLTASRV LGAELQARGH DALIAESLAA L DRRN UniProtKB: ATP synthase subunit b |
-Macromolecule #2: ATP synthase subunit a
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase subunit a / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.176105 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSTRTRNILI IVGALIISIA SRFFLYTGPP HVEVAAEVIF DGIPGFPITN SFVVAIIIDI FVIALAVAAT RNLQMVPRGL QNVMEFILE SLYNLFRNIN AKYVATAFPL VATIFLFVLF GNWFGLLPGV GSIGVCHEKK EEHAVVDERL ALAAPAAPLS S VAAAEGEE ...String: MSTRTRNILI IVGALIISIA SRFFLYTGPP HVEVAAEVIF DGIPGFPITN SFVVAIIIDI FVIALAVAAT RNLQMVPRGL QNVMEFILE SLYNLFRNIN AKYVATAFPL VATIFLFVLF GNWFGLLPGV GSIGVCHEKK EEHAVVDERL ALAAPAAPLS S VAAAEGEE IHDTCAAQGK KLVPLFRAPA ADLNFTFAIA VISFVFIEYW GFRALGPGYL KKFFNTNGIM SFVGIIEFIS EL VKPFALA FRLFGNIFAG EVLLVVMAFL VPLLLPLPFY GFEVFVGFIQ ALIFALLTYA FLNIAVTGHD EEHAH UniProtKB: ATP synthase subunit a |
-Macromolecule #3: ATP synthase subunit c
| Macromolecule | Name: ATP synthase subunit c / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 10 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) Chloroflexus aurantiacus J-10-fl (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 7.688102 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MEGLNLVATA LAVGLGAIGP GVGIGIIVSG AVQAIGRNPE IENRVVTYMF IGIAFTEALA IFGLVIAFLI GFGVLQ UniProtKB: ATP synthase subunit c |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.6 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)