+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Membrane / Complex / Native / Synaptic / PROTON TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / transporter activator activity / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation ...regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / transporter activator activity / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / intracellular organelle / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / lysosomal lumen acidification / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / neuron spine / head morphogenesis / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / protein localization to cilium / regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / vacuolar acidification / neuron projection terminus / dendritic spine membrane / regulation of cellular pH / syntaxin-1 binding / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Neutrophil degranulation / cholesterol binding / ATPase complex / regulation of MAPK cascade / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / presynaptic active zone / response to amyloid-beta / ATPase activator activity / microvillus / autophagosome membrane / excitatory synapse / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / cilium assembly / transmembrane transporter complex / regulation of macroautophagy / angiotensin maturation / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / ATP metabolic process / axon terminus / ruffle / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / RNA endonuclease activity / SH2 domain binding / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / receptor-mediated endocytosis / proton transmembrane transport / SNARE binding / secretory granule / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / neuromuscular junction / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / terminal bouton / transmembrane transport / cilium / small GTPase binding / synaptic vesicle membrane / endocytosis / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / melanosome / synaptic vesicle / apical part of cell / presynapse / signaling receptor activity / presynaptic membrane / ATPase binding / cell body / postsynaptic membrane / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / lysosome / early endosome / postsynaptic density / endosome membrane / endosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
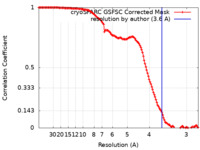
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Coupland CE / Rubinstein JL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles. Authors: Claire E Coupland / Ryan Karimi / Stephanie A Bueler / Yingke Liang / Gautier M Courbon / Justin M Di Trani / Cassandra J Wong / Rayan Saghian / Ji-Young Youn / Lu-Yang Wang / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or ...Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) powers neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicles (SVs), with the V complex dissociating from the membrane region of the enzyme before exocytosis. We isolated SVs from rat brain using SidK, a V-ATPase-binding bacterial effector protein. Single-particle electron cryomicroscopy allowed high-resolution structure determination of V-ATPase within the native SV membrane. In the structure, regularly spaced cholesterol molecules decorate the enzyme's rotor and the abundant SV protein synaptophysin binds the complex stoichiometrically. ATP hydrolysis during vesicle loading results in a loss of the V region of V-ATPase from the SV membrane, suggesting that loading is sufficient to induce dissociation of the enzyme. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
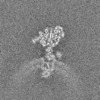
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44355.map.gz emd_44355.map.gz | 203.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44355-v30.xml emd-44355-v30.xml emd-44355.xml emd-44355.xml | 13.1 KB 13.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44355_fsc.xml emd_44355_fsc.xml | 12.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44355.png emd_44355.png | 104.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44355.cif.gz emd-44355.cif.gz | 3.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44355_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44355_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44355_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44355_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.5 MB 200.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44355 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44355 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44355 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44355 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_44355_validation.pdf.gz emd_44355_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_44355_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_44355_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_44355_validation.xml.gz emd_44355_validation.xml.gz | 21.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_44355_validation.cif.gz emd_44355_validation.cif.gz | 28 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44355 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44355 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44355 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-44355 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9brbMC  9b8oC  9b8pC  9b8qC  9brcC  9brdC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44355.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44355.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.37333 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
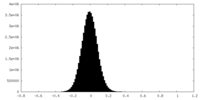
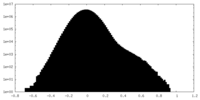
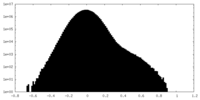
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44355_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44355_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3
| Entire | Name: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3
| Supramolecule | Name: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: TFS FALCON 4i (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 37.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.9000000000000001 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)