+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3639 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
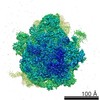
| Title | 100S disome from Staphylococcus aureus (Loose conformation) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Khusainov I / Vicens Q / Ayupov R / Usachev K / Myasnikov A / Simonetti A / Validov S / Kieffer B / Yusupova G / Yusupov M / Hashem Y | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2017 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2017Title: Structures and dynamics of hibernating ribosomes from mediated by intermolecular interactions of HPF. Authors: Iskander Khusainov / Quentin Vicens / Rustam Ayupov / Konstantin Usachev / Alexander Myasnikov / Angelita Simonetti / Shamil Validov / Bruno Kieffer / Gulnara Yusupova / Marat Yusupov / Yaser Hashem /   Abstract: In bacteria, ribosomal hibernation shuts down translation as a response to stress, through reversible binding of stress-induced proteins to ribosomes. This process typically involves the formation of ...In bacteria, ribosomal hibernation shuts down translation as a response to stress, through reversible binding of stress-induced proteins to ribosomes. This process typically involves the formation of 100S ribosome dimers. Here, we present the structures of hibernating ribosomes from human pathogen containing a long variant of the hibernation-promoting factor (SaHPF) that we solved using cryo-electron microscopy. Our reconstructions reveal that the N-terminal domain (NTD) of SaHPF binds to the 30S subunit as observed for shorter variants of HPF in other species. The C-terminal domain (CTD) of SaHPF protrudes out of each ribosome in order to mediate dimerization. Using NMR, we characterized the interactions at the CTD-dimer interface. Secondary interactions are provided by helix 26 of the 16S ribosomal RNA We also show that ribosomes in the 100S particle adopt both rotated and unrotated conformations. Overall, our work illustrates a specific mode of ribosome dimerization by long HPF, a finding that may help improve the selectivity of antimicrobials. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3639.map.gz emd_3639.map.gz | 28.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3639-v30.xml emd-3639-v30.xml emd-3639.xml emd-3639.xml | 11.5 KB 11.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3639.png emd_3639.png | 288.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3639 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3639 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3639 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3639 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_3639_validation.pdf.gz emd_3639_validation.pdf.gz | 282.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_3639_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_3639_full_validation.pdf.gz | 281.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_3639_validation.xml.gz emd_3639_validation.xml.gz | 5.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3639 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3639 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3639 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-3639 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  3624C  3625C 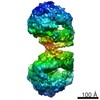 3638C  5nd8C  5nd9C  5nkoC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3639.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3639.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 100S disome from Staphylococcus aureus (Loose conformation)
| Entire | Name: 100S disome from Staphylococcus aureus (Loose conformation) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 100S disome from Staphylococcus aureus (Loose conformation)
| Supramolecule | Name: 100S disome from Staphylococcus aureus (Loose conformation) type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: S. aureus 100S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: S. aureus 100S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Details: Two vacant 70S ribosomes dimerized via SaHPF |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) |
-Supramolecule #3: Ribosome hibernation promoting factor (SaHPF)
| Supramolecule | Name: Ribosome hibernation promoting factor (SaHPF) / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus (strain NCTC 8325) (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 5 mM Hepes-KOH pH 7.5 50 mM KCl 10 mM NH4Cl 10 mM Mg(OAc)2 1 mM DTT |
|---|---|
| Grid | Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot force 5, blot waiting time 30 s. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 2-8 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Average exposure time: 1.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)