[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-25384: Structure of the human proton-activated chloride channel ASOR in ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-25384 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of the human proton-activated chloride channel ASOR in resting conformation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | final map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / chloride channel / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | pH-gated chloride channel activity / TMEM206 protein / TMEM206 protein family / chloride transport / chloride channel complex / cell surface / plasma membrane / Proton-activated chloride channel Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Long SB / Wang C | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022Title: Gating choreography and mechanism of the human proton-activated chloride channel ASOR. Authors: Chongyuan Wang / Maya M Polovitskaya / Bryce D Delgado / Thomas J Jentsch / Stephen B Long /   Abstract: The proton-activated chloride channel ASOR (TMEM206/PAC) permeates anions across cellular membranes in response to acidification, thereby enhancing acid-induced cell death and regulating endocytosis. ...The proton-activated chloride channel ASOR (TMEM206/PAC) permeates anions across cellular membranes in response to acidification, thereby enhancing acid-induced cell death and regulating endocytosis. The molecular mechanisms of pH-dependent control are not understood, in part because structural information for an activated conformation of ASOR is lacking. Here, we reconstitute function from purified protein and present a 3.1-Å-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of human ASOR at acidic pH in an activated conformation. The work contextualizes a previous acidic pH structure as a desensitized conformation. Combined with electrophysiological studies and high-resolution structures of resting and desensitized states, the work reveals mechanisms of proton sensing and ion pore gating. Clusters of extracellular acidic residues function as pH sensors and coalesce when protonated. Ensuing conformational changes induce metamorphosis of transmembrane helices to fashion an ion conduction pathway unique to the activated conformation. The studies identify a new paradigm of channel gating in this ubiquitous ion channel. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_25384.map.gz emd_25384.map.gz | 192.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-25384-v30.xml emd-25384-v30.xml emd-25384.xml emd-25384.xml | 14.1 KB 14.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_25384.png emd_25384.png | 91 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-25384.cif.gz emd-25384.cif.gz | 5.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25384 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25384 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25384 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25384 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_25384_validation.pdf.gz emd_25384_validation.pdf.gz | 329.1 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_25384_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25384_full_validation.pdf.gz | 328.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_25384_validation.xml.gz emd_25384_validation.xml.gz | 7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_25384_validation.cif.gz emd_25384_validation.cif.gz | 8.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25384 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25384 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25384 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25384 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 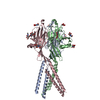 7sqgMC 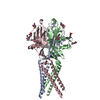 7sqfC  7sqhC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_25384.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_25384.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | final map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : proton activated chloride channel TMEM206 in resting conformation
| Entire | Name: proton activated chloride channel TMEM206 in resting conformation |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: proton activated chloride channel TMEM206 in resting conformation
| Supramolecule | Name: proton activated chloride channel TMEM206 in resting conformation type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Proton-activated chloride channel
| Macromolecule | Name: Proton-activated chloride channel / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.092047 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MIRQERSTSY QELSEELVQV VENSELADEQ DKETVRVQGP GILPGLDSES ASSSIRFSKA CLKNVFSVLL IFIYLLLMAV AVFLVYRTI TDFREKLKHP VMSVSYKEVD RYDAPGIALY PGQAQLLSCK HHYEVIPPLT SPGQPGDMNC TTQRINYTDP F SNQTVKSA ...String: MIRQERSTSY QELSEELVQV VENSELADEQ DKETVRVQGP GILPGLDSES ASSSIRFSKA CLKNVFSVLL IFIYLLLMAV AVFLVYRTI TDFREKLKHP VMSVSYKEVD RYDAPGIALY PGQAQLLSCK HHYEVIPPLT SPGQPGDMNC TTQRINYTDP F SNQTVKSA LIVQGPREVK KRELVFLQFR LNKSSEDFSA IDYLLFSSFQ EFLQSPNRVG FMQACESAYS SWKFSGGFRT WV KMSLVKT KEEDGREAVE FRQETSVVNY IDQRPAAKKS AQLFFVVFEW KDPFIQKVQD IVTANPWNTI ALLCGAFLAL FKA AEFAKL SIKWMIKIRK RYLKRRGQAT SHIS UniProtKB: Proton-activated chloride channel |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5.0 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 2 second blot, blot force of 0. | |||||||||
| Details | Monodisperse sample |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 60374 / Average exposure time: 1.8 sec. / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 30 / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7sqg: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


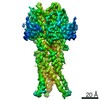
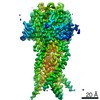




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)