[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24726: afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+ -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+ | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Used for the building of the protein part and some lipids in the model | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TMEM16 / lipid scrambling / LIPID TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphospholipid scramblase activity / cortical endoplasmic reticulum / phospholipid translocation / chloride channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / chloride transmembrane transport / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.08 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Feng Z / Accardi A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: TMEM16 scramblases thin the membrane to enable lipid scrambling. Authors: Maria E Falzone / Zhang Feng / Omar E Alvarenga / Yangang Pan / ByoungCheol Lee / Xiaolu Cheng / Eva Fortea / Simon Scheuring / Alessio Accardi /   Abstract: TMEM16 scramblases dissipate the plasma membrane lipid asymmetry to activate multiple eukaryotic cellular pathways. Scrambling was proposed to occur with lipid headgroups moving between leaflets ...TMEM16 scramblases dissipate the plasma membrane lipid asymmetry to activate multiple eukaryotic cellular pathways. Scrambling was proposed to occur with lipid headgroups moving between leaflets through a membrane-spanning hydrophilic groove. Direct information on lipid-groove interactions is lacking. We report the 2.3 Å resolution cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the nanodisc-reconstituted Ca-bound afTMEM16 scramblase showing how rearrangement of individual lipids at the open pathway results in pronounced membrane thinning. Only the groove's intracellular vestibule contacts lipids, and mutagenesis suggests scrambling does not require specific protein-lipid interactions with the extracellular vestibule. We find scrambling can occur outside a closed groove in thinner membranes and is inhibited in thicker membranes, despite an open pathway. Our results show afTMEM16 thins the membrane to enable scrambling and that an open hydrophilic pathway is not a structural requirement to allow rapid transbilayer movement of lipids. This mechanism could be extended to other scramblases lacking a hydrophilic groove. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24726.map.gz emd_24726.map.gz | 59.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24726-v30.xml emd-24726-v30.xml emd-24726.xml emd-24726.xml | 13.9 KB 13.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24726_fsc.xml emd_24726_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24726.png emd_24726.png | 98.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24726.cif.gz emd-24726.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24726_additional_1.map.gz emd_24726_additional_1.map.gz | 48.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24726 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24726 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24726 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24726 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24726_validation.pdf.gz emd_24726_validation.pdf.gz | 586.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24726_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24726_full_validation.pdf.gz | 586.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24726_validation.xml.gz emd_24726_validation.xml.gz | 10.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24726_validation.cif.gz emd_24726_validation.cif.gz | 14.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24726 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24726 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24726 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24726 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7rxaMC  7rwjC  7rx2C  7rx3C  7rxbC  7rxgC  7rxhC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24726.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24726.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Used for the building of the protein part and some lipids in the model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Used for the building of some lipids in the model
| File | emd_24726_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Used for the building of some lipids in the model | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
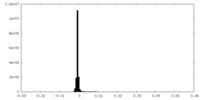
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+
| Entire | Name: afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+ |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+
| Supramolecule | Name: afTMEM16 DE/AA mutant in C14 lipid nanodiscs in the presence of Ca2+ type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: afTMEM16 lipid scramblase
| Macromolecule | Name: afTMEM16 lipid scramblase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: CEA10 / CBS 144.89 / FGSC A1163 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 84.514812 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAFNPAPKAV QENHHVDYVI RFNYGDIDTP EAIKKFEVLL LELSEVGLQT EVRQGDENSL FVFVRAASKK KLKRAVYQSR VRDWLYGVR NTEPEPASSA KPQSEAERLL VIYHLITVPK AEGGAGITPR HGEWKNVDAI FPLHDEETNR QCMREWSKKT F LSTEDLDR ...String: MAFNPAPKAV QENHHVDYVI RFNYGDIDTP EAIKKFEVLL LELSEVGLQT EVRQGDENSL FVFVRAASKK KLKRAVYQSR VRDWLYGVR NTEPEPASSA KPQSEAERLL VIYHLITVPK AEGGAGITPR HGEWKNVDAI FPLHDEETNR QCMREWSKKT F LSTEDLDR IRNTFGEHVG FYFAFLQSYF RFLMFPAAFG FSCWLLLGSF SIIYTVVNCL WCIVFIEYWK RQEEDLSCRW QT KGVSAVH EKRAEFKPEK EIRDESTGEV RGVFPATKRM YRQLLQVPFA LLAAVALGAI IATCFAIEIF ISEVYNGPLK GYL VFIPTI LVSALIPTMS AVLLTVATKL NDYENYETQD AYKVALTQKI FVVNFITSYL PIILTAFVYV PFASRIVPYL DVFH LTVRP FVSKEHAIKA RTEFSINPDR LRKQVIYFTV TAQIVGFALE TIVPFVKQRV FREYKEYTKK QHAKAEPGNG AGEKK TVSL GDDEDEARFL TRVRNEAELE DYDVTDALRA MCIQFGYLAL FSPVWPLVPV SFLINNWVEL RSDFFKICVE CKRPWP QRA DTIGPWLDSL GFLSWVGSIT SSALVYMFSN GHEGPNGEPT TIRCWALLLT IFFSEHLYLI VRYAVRSALA KLEPPNT RR ERIERFMMRK RYLDTVLSAE SDDDADEVKG VVSSIPPSEI TRESLEQDAR DWSKQGTDPT ERFWMRQRGW KESAEVGL S LITKAKGDET KKQQ UniProtKB: Plasma membrane channel protein (Aqy1), putative |
-Macromolecule #2: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]o...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(hexadecanoyloxy)methyl]ethyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: PGW |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 749.007 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 42.18 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)