[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24544: RACK1-S278E, reconstruction from 40S particles (filtered accordin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24544 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
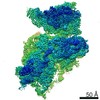
| Title | RACK1-S278E, reconstruction from 40S particles (filtered according to local resolution) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | RACK1-S278E 40S particles | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shen PS / Rollins MG / Shasmal M / Meade N / Astar H / Walsh D | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2021 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2021Title: Negative charge in the RACK1 loop broadens the translational capacity of the human ribosome. Authors: Madeline G Rollins / Manidip Shasmal / Nathan Meade / Helen Astar / Peter S Shen / Derek Walsh /  Abstract: Although the roles of initiation factors, RNA binding proteins, and RNA elements in regulating translation are well defined, how the ribosome functionally diversifies remains poorly understood. In ...Although the roles of initiation factors, RNA binding proteins, and RNA elements in regulating translation are well defined, how the ribosome functionally diversifies remains poorly understood. In their human hosts, poxviruses phosphorylate serine 278 (S) at the tip of a loop domain in the small subunit ribosomal protein RACK1, thereby mimicking negatively charged residues in the RACK1 loops of dicot plants and protists to stimulate translation of transcripts with 5' poly(A) leaders. However, how a negatively charged RACK1 loop affects ribosome structure and its broader translational output is not known. Here, we show that although ribotoxin-induced stress signaling and stalling on poly(A) sequences are unaffected, negative charge in the RACK1 loop alters the swivel motion of the 40S head domain in a manner similar to several internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs), confers resistance to various protein synthesis inhibitors, and broadly supports noncanonical modes of translation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24544.map.gz emd_24544.map.gz | 132.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24544-v30.xml emd-24544-v30.xml emd-24544.xml emd-24544.xml | 10.7 KB 10.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_24544.png emd_24544.png | 42.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24544 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24544 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24544 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24544 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24544_validation.pdf.gz emd_24544_validation.pdf.gz | 296.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24544_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24544_full_validation.pdf.gz | 296.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24544_validation.xml.gz emd_24544_validation.xml.gz | 7.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24544_validation.cif.gz emd_24544_validation.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24544 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24544 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24544 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24544 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24544.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24544.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | RACK1-S278E 40S particles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.348 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RACK1-S278E 80S rotated state, consensus reconstruction
| Entire | Name: RACK1-S278E 80S rotated state, consensus reconstruction |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RACK1-S278E 80S rotated state, consensus reconstruction
| Supramolecule | Name: RACK1-S278E 80S rotated state, consensus reconstruction type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.5 MDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 5.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 16758 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




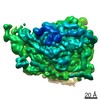
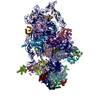

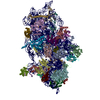
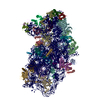




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















