[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24418: Microtubule subtomogram average of deconvolved particles, randomi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24418 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
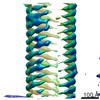
| Title | Microtubule subtomogram average of deconvolved particles, randomized starting azimuth and restricted angular search | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
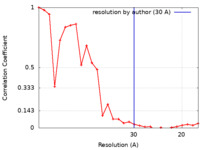
| Method | subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 30.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Croxford M / Villa E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Entropy-regularized deconvolution of cellular cryotransmission electron tomograms. Authors: Matthew Croxford / Michael Elbaum / Muthuvel Arigovindan / Zvi Kam / David Agard / Elizabeth Villa / John Sedat /    Abstract: Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) allows for the high-resolution visualization of biological macromolecules. However, the technique is limited by a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and variance in ...Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) allows for the high-resolution visualization of biological macromolecules. However, the technique is limited by a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and variance in contrast at different frequencies, as well as reduced Z resolution. Here, we applied entropy-regularized deconvolution (ER-DC) to cryo-ET data generated from transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and reconstructed using weighted back projection (WBP). We applied deconvolution to several in situ cryo-ET datasets and assessed the results by Fourier analysis and subtomogram analysis (STA). | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24418.map.gz emd_24418.map.gz | 775 KB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24418-v30.xml emd-24418-v30.xml emd-24418.xml emd-24418.xml | 13.7 KB 13.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24418_fsc.xml emd_24418_fsc.xml | 2.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24418.png emd_24418.png | 37 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_24418_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24418_half_map_1.map.gz emd_24418_half_map_2.map.gz emd_24418_half_map_2.map.gz | 780.1 KB 778.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24418 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24418 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24418 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24418 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24418_validation.pdf.gz emd_24418_validation.pdf.gz | 451.2 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24418_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24418_full_validation.pdf.gz | 450.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24418_validation.xml.gz emd_24418_validation.xml.gz | 8.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24418_validation.cif.gz emd_24418_validation.cif.gz | 10.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24418 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24418 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24418 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24418 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24418.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 844.7 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24418.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 844.7 KB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
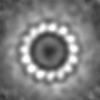
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 8.984 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
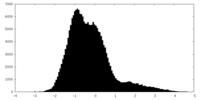
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_24418_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
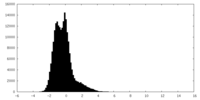
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_24418_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
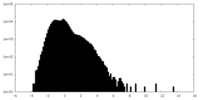
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Microtubule
| Entire | Name: Microtubule |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Microtubule
| Supramolecule | Name: Microtubule / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Details: Subtomogram average of a polymerized microtubule. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293 / Organ: Kidney Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293 / Organ: Kidney |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | subtomogram averaging |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Support film - Material: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 96.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)