[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23837: Human Hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT) in complex with a palmitoyl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23837 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human Hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT) in complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide product and a Fab antibody fragment | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | final map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MBOAT / GOAT / porcupine / acyl transferase / membrane protein / membrane enzyme / ER / palmitoyl-CoA / TRANSFERASE-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationN-terminal peptidyl-L-cysteine N-palmitoylation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation ...N-terminal peptidyl-L-cysteine N-palmitoylation / positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation / right lung development / left lung development / primary prostatic bud elongation / regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / mesenchymal smoothened signaling pathway involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of sclerotome development / tracheoesophageal septum formation / negative regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation / negative regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of kidney smooth muscle cell differentiation / morphogen activity / regulation of odontogenesis / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development / O-acyltransferase activity / trunk neural crest cell migration / Formation of lateral plate mesoderm / hindgut morphogenesis / polarity specification of anterior/posterior axis / striated muscle tissue development / negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell differentiation / regulation of glial cell proliferation / regulation of prostatic bud formation / metanephric mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in metanephros development / formation of anatomical boundary / lung epithelium development / positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation / ventral midline development / trachea morphogenesis / cholesterol-protein transferase activity / bud outgrowth involved in lung branching / HHAT G278V doesn't palmitoylate Hh-Np / telencephalon regionalization / epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling / Ligand-receptor interactions / laminin-1 binding / negative regulation of cholesterol efflux / salivary gland cavitation / spinal cord dorsal/ventral patterning / negative regulation of mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / determination of left/right asymmetry in lateral mesoderm / positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / palmitoyltransferase activity / spinal cord motor neuron differentiation / positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / cell development / intermediate filament organization / prostate gland development / cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation / limb bud formation / Activation of SMO / lung lobe morphogenesis / embryonic skeletal system development / establishment of epithelial cell polarity / skeletal muscle fiber differentiation / mesenchymal cell apoptotic process / patched binding / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / somite development / epithelial cell proliferation involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / animal organ formation / embryonic foregut morphogenesis / hindbrain development / neuron fate commitment / ectoderm development / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development / thalamus development / stem cell development / mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development / negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation / dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus / CD4-positive or CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment / smooth muscle tissue development / negative thymic T cell selection / pattern specification process / artery development / oligodendrocyte development / positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation / male genitalia development / regulation of stem cell proliferation / self proteolysis / epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development / embryonic pattern specification / branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis / Release of Hh-Np from the secreting cell / dopaminergic neuron differentiation / lung-associated mesenchyme development / glycosaminoglycan binding / Formation of axial mesoderm / regulation of proteolysis / intein-mediated protein splicing / metanephric collecting duct development / metanephros development Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Long SB / Jiang Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2021 Journal: Science / Year: 2021Title: Substrate and product complexes reveal mechanisms of Hedgehog acylation by HHAT. Authors: Yiyang Jiang / Thomas L Benz / Stephen B Long /  Abstract: Hedgehog proteins govern crucial developmental steps in animals and drive certain human cancers. Before they can function as signaling molecules, Hedgehog precursor proteins must undergo amino- ...Hedgehog proteins govern crucial developmental steps in animals and drive certain human cancers. Before they can function as signaling molecules, Hedgehog precursor proteins must undergo amino-terminal palmitoylation by Hedgehog acyltransferase (HHAT). We present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human HHAT in complex with its palmitoyl-coenzyme A substrate and of a product complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide at resolutions of 2.7 and 3.2 angstroms, respectively. The structures reveal how HHAT overcomes the challenges of bringing together substrates that have different physiochemical properties from opposite sides of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane within a membrane-embedded active site for catalysis. These principles are relevant to related enzymes that catalyze the acylation of Wnt and of the appetite-stimulating hormone ghrelin. The structural and mechanistic insights may advance the development of inhibitors for cancer. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23837.map.gz emd_23837.map.gz | 187.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23837-v30.xml emd-23837-v30.xml emd-23837.xml emd-23837.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23837.png emd_23837.png | 118.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23837.cif.gz emd-23837.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23837 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23837 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_23837_validation.pdf.gz emd_23837_validation.pdf.gz | 493.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_23837_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_23837_full_validation.pdf.gz | 493 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_23837_validation.xml.gz emd_23837_validation.xml.gz | 7.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_23837_validation.cif.gz emd_23837_validation.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23837 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23837 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23837 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mhzMC  7mhyC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23837.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 204.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23837.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 204.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | final map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.532 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : HHAT in complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide product and...
| Entire | Name: HHAT in complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide product and a Fab antibody fragment |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: HHAT in complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide product and...
| Supramolecule | Name: HHAT in complex with a palmitoylated Hedgehog peptide product and a Fab antibody fragment type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sonic hedgehog protein N-product peptide
| Macromolecule | Name: Sonic hedgehog protein N-product peptide / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 750.848 Da |
| Sequence | String: CGPGRGFG UniProtKB: Sonic hedgehog protein |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein-cysteine N-palmitoyltransferase HHAT
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein-cysteine N-palmitoyltransferase HHAT / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 57.358742 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MLPRWELALY LLASLGFHFY SFYEVYKVSR EHEEELDQEF ELETDTLFGG LKKDATDFEW SFWMEWGKQW LVWLLLGHMV VSQMATLLA RKHRPWILML YGMWACWCVL GTPGVAMVLL HTTISFCVAQ FRSQLLTWLC SLLLLSTLRL QGVEEVKRRW Y KTENEYYL ...String: MLPRWELALY LLASLGFHFY SFYEVYKVSR EHEEELDQEF ELETDTLFGG LKKDATDFEW SFWMEWGKQW LVWLLLGHMV VSQMATLLA RKHRPWILML YGMWACWCVL GTPGVAMVLL HTTISFCVAQ FRSQLLTWLC SLLLLSTLRL QGVEEVKRRW Y KTENEYYL LQFTLTVRCL YYTSFSLELC WQQLPAASTS YSFPWMLAYV FYYPVLHNGP ILSFSEFIKQ MQQQEHDSLK AS LCVLALG LGRLLCWWWL AELMAHLMYM HAIYSSIPLL ETVSCWTLGG LALAQVLFFY VKYLVLFGVP ALLMRLDGLT PPA LPRCVS TMFSFTGMWR YFDVGLHNFL IRYVYIPVGG SQHGLLGTLF STAMTFAFVS YWHGGYDYLW CWAALNWLGV TVEN GVRRL VETPCIQDSL ARYFSPQARR RFHAALASCS TSMLILSNLV FLGGNEVGKT YWNRIFIQGW PWVTLSVLGF LYCYS HVGI AWAQTYATD UniProtKB: Protein-cysteine N-palmitoyltransferase HHAT |
-Macromolecule #3: 3H02 Fab heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: 3H02 Fab heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.307891 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGWSCIILFL VATATGVHSQ IQLVQSGPEL KKPGETVKIS CKASGYTFTN YGMNWVRQAP GKGLKWMGWI NTYTGEPTYA DDFKGRFAF SLETSASTAY LQINNLKDED MATYFCARVW NYDYYFDYWG QGTTLTVSSA KTTPPSVYPL APGSAAQTNS M VTLGCLVK ...String: MGWSCIILFL VATATGVHSQ IQLVQSGPEL KKPGETVKIS CKASGYTFTN YGMNWVRQAP GKGLKWMGWI NTYTGEPTYA DDFKGRFAF SLETSASTAY LQINNLKDED MATYFCARVW NYDYYFDYWG QGTTLTVSSA KTTPPSVYPL APGSAAQTNS M VTLGCLVK GYFPEPVTVT WNSGSLSSGV HTFPAVLQSD LYTLSSSVTV PSSPRPSETV TCNVAHPASS TKVDKKIVPR DC GCKPCIC TVPEVSSVFI FPPKPKDVLT ITLTPKVTCV VVDISKDDPE VQFSWFVDDV EVHTAQTQPR EEQFNSTFRS VSE LPIMHQ DWLNGKEFKC RVNSAAFPAP IEKTISKTKG RPKAPQVYTI PPPKEQMAKD KVSLTCMITD FFPEDITVEW QWNG QPAEN YKNTQPIMNT NGSYFVYSKL NVQKSNWEAG NTFTCSVLHE GLHNHHTEKS LSHSPGK |
-Macromolecule #4: 3H02 Fab light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: 3H02 Fab light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.868863 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKLPVRLLVL MFWIPASRSD VLMTQTPLSL PVSLGDQVSI SCRSSQSIVH SNGNTYLEWY LQKPGQSPKL LIYRVSNRFS GVPDRFSGS GSGTDFTLKI SRVEAEDLGV YYCFQGSHVP WTFGGGTKLE IKRADAAPTV SIFPPSSEQL TSGGASVVCF L NNFYPKDI ...String: MKLPVRLLVL MFWIPASRSD VLMTQTPLSL PVSLGDQVSI SCRSSQSIVH SNGNTYLEWY LQKPGQSPKL LIYRVSNRFS GVPDRFSGS GSGTDFTLKI SRVEAEDLGV YYCFQGSHVP WTFGGGTKLE IKRADAAPTV SIFPPSSEQL TSGGASVVCF L NNFYPKDI NVKWKIDGSE RQNGVLNSWT DQDSKDSTYS MSSTLTLTK |
-Macromolecule #5: PALMITIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: PALMITIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PLM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.424 Da |
| Chemical component information | 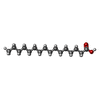 ChemComp-PLM: |
-Macromolecule #6: PROTOPORPHYRIN IX CONTAINING FE
| Macromolecule | Name: PROTOPORPHYRIN IX CONTAINING FE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: HEM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 616.487 Da |
| Chemical component information | 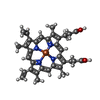 ChemComp-HEM: |
-Macromolecule #7: Palmitoyl-CoA
| Macromolecule | Name: Palmitoyl-CoA / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: PKZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.005943 KDa |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PKZ: |
-Macromolecule #8: Digitonin
| Macromolecule | Name: Digitonin / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 10 / Formula: AJP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.229312 KDa |
| Chemical component information | 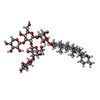 ChemComp-AJP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 43.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 142121 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)





















