+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23618 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
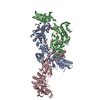
| Title | Human ABCA4 structure in complex with N-ret-PE | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ABC transporter / importer / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationrod photoreceptor disc membrane / flippase activity / N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / all-trans retinal binding / phospholipid transfer to membrane / retinol transmembrane transporter activity / phospholipid transporter activity / 11-cis retinal binding / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / retinal metabolic process ...rod photoreceptor disc membrane / flippase activity / N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / all-trans retinal binding / phospholipid transfer to membrane / retinol transmembrane transporter activity / phospholipid transporter activity / 11-cis retinal binding / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / retinal metabolic process / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / phototransduction, visible light / retinoid binding / P-type phospholipid transporter / photoreceptor cell maintenance / phospholipid translocation / retinoid metabolic process / lipid transport / Retinoid cycle disease events / The canonical retinoid cycle in rods (twilight vision) / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / photoreceptor outer segment / ABC-type transporter activity / visual perception / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / transmembrane transport / photoreceptor disc membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / GTPase activity / endoplasmic reticulum / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.92 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Scortecci JF / Van Petegem F | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structures of the ABCA4 importer reveal mechanisms underlying substrate binding and Stargardt disease. Authors: Jessica Fernandes Scortecci / Laurie L Molday / Susan B Curtis / Fabian A Garces / Pankaj Panwar / Filip Van Petegem / Robert S Molday /  Abstract: ABCA4 is an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter that flips N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-Ret-PE) from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of photoreceptor membranes. Loss-of-function ...ABCA4 is an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter that flips N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-Ret-PE) from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of photoreceptor membranes. Loss-of-function mutations cause Stargardt disease (STGD1), a macular dystrophy associated with severe vision loss. To define the mechanisms underlying substrate binding and STGD1, we determine the cryo-EM structure of ABCA4 in its substrate-free and bound states. The two structures are similar and delineate an elongated protein with the two transmembrane domains (TMD) forming an outward facing conformation, extended and twisted exocytoplasmic domains (ECD), and closely opposed nucleotide binding domains. N-Ret-PE is wedged between the two TMDs and a loop from ECD1 within the lumen leaflet consistent with a lateral access mechanism and is stabilized through hydrophobic and ionic interactions with residues from the TMDs and ECDs. Our studies provide a framework for further elucidating the molecular mechanism associated with lipid transport and disease and developing promising disease interventions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23618.map.gz emd_23618.map.gz | 211.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23618-v30.xml emd-23618-v30.xml emd-23618.xml emd-23618.xml | 13.1 KB 13.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_23618_fsc.xml emd_23618_fsc.xml | 16.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_23618.png emd_23618.png | 23.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23618.cif.gz emd-23618.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23618 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23618 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23618 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23618 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_23618_validation.pdf.gz emd_23618_validation.pdf.gz | 514 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_23618_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_23618_full_validation.pdf.gz | 513.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_23618_validation.xml.gz emd_23618_validation.xml.gz | 15.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_23618_validation.cif.gz emd_23618_validation.cif.gz | 21.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23618 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23618 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23618 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23618 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7m1qMC  7m1pC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23618.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23618.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.77219 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ABCA4 structure in complex with N-ret-PE
| Entire | Name: ABCA4 structure in complex with N-ret-PE |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ABCA4 structure in complex with N-ret-PE
| Supramolecule | Name: ABCA4 structure in complex with N-ret-PE / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: Recombinantly expressed human ABCA4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 250 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Retinal-specific phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA4
| Macromolecule | Name: Retinal-specific phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA4 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 256.202531 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGFVRQIQLL LWKNWTLRKR QKIRFVVELV WPLSLFLVLI WLRNANPLYS HHECHFPNKA MPSAGMLPWL QGIFCNVNNP CFQSPTPGE SPGIVSNYNN SILARVYRDF QELLMNAPES QHLGRIWTEL HILSQFMDTL RTHPERIAGR GIRIRDILKD E ETLTLFLI ...String: MGFVRQIQLL LWKNWTLRKR QKIRFVVELV WPLSLFLVLI WLRNANPLYS HHECHFPNKA MPSAGMLPWL QGIFCNVNNP CFQSPTPGE SPGIVSNYNN SILARVYRDF QELLMNAPES QHLGRIWTEL HILSQFMDTL RTHPERIAGR GIRIRDILKD E ETLTLFLI KNIGLSDSVV YLLINSQVRP EQFAHGVPDL ALKDIACSEA LLERFIIFSQ RRGAKTVRYA LCSLSQGTLQ WI EDTLYAN VDFFKLFRVL PTLLDSRSQG INLRSWGGIL SDMSPRIQEF IHRPSMQDLL WVTRPLMQNG GPETFTKLMG ILS DLLCGY PEGGGSRVLS FNWYEDNNYK AFLGIDSTRK DPIYSYDRRT TSFCNALIQS LESNPLTKIA WRAAKPLLMG KILY TPDSP AARRILKNAN STFEELEHVR KLVKAWEEVG PQIWYFFDNS TQMNMIRDTL GNPTVKDFLN RQLGEEGITA EAILN FLYK GPRESQADDM ANFDWRDIFN ITDRTLRLVN QYLECLVLDK FESYNDETQL TQRALSLLEE NMFWAGVVFP DMYPWT SSL PPHVKYKIRM DIDVVEKTNK IKDRYWDSGP RADPVEDFRY IWGGFAYLQD MVEQGITRSQ VQAEAPVGIY LQQMPYP CF VDDSFMIILN RCFPIFMVLA WIYSVSMTVK SIVLEKELRL KETLKNQGVS NAVIWCTWFL DSFSIMSMSI FLLTIFIM H GRILHYSDPF ILFLFLLAFS TATIMLCFLL STFFSKASLA AACSGVIYFT LYLPHILCFA WQDRMTAELK KAVSLLSPV AFGFGTEYLV RFEEQGLGLQ WSNIGNSPTE GDEFSFLLSM QMMLLDAAVY GLLAWYLDQV FPGDYGTPLP WYFLLQESYW LGGEGCSTR EERALEKTEP LTEETEDPEH PEGIHDSFFE REHPGWVPGV CVKNLVKIFE PCGRPAVDRL NITFYENQIT A FLGHNGAG KTTTLSILTG LLPPTSGTVL VGGRDIETSL DAVRQSLGMC PQHNILFHHL TVAEHMLFYA QLKGKSQEEA QL EMEAMLE DTGLHHKRNE EAQDLSGGMQ RKLSVAIAFV GDAKVVILDE PTSGVDPYSR RSIWDLLLKY RSGRTIIMST HHM DEADLL GDRIAIIAQG RLYCSGTPLF LKNCFGTGLY LTLVRKMKNI QSQRKGSEGT CSCSSKGFST TCPAHVDDLT PEQV LDGDV NELMDVVLHH VPEAKLVECI GQELIFLLPN KNFKHRAYAS LFRELEETLA DLGLSSFGIS DTPLEEIFLK VTEDS DSGP LFAGGAQQKR ENVNPRHPCL GPREKAGQTP QDSNVCSPGA PAAHPEGQPP PEPECPGPQL NTGTQLVLQH VQALLV KRF QHTIRSHKDF LAQIVLPATF VFLALMLSIV IPPFGEYPAL TLHPWIYGQQ YTFFSMDEPG SEQFTVLADV LLNKPGF GN RCLKEGWLPE YPCGNSTPWK TPSVSPNITQ LFQKQKWTQV NPSPSCRCST REKLTMLPEC PEGAGGLPPP QRTQRSTE I LQDLTDRNIS DFLVKTYPAL IRSSLKSKFW VNEQRYGGIS IGGKLPVVPI TGEALVGFLS DLGRIMNVSG GPITREASK EIPDFLKHLE TEDNIKVWFN NKGWHALVSF LNVAHNAILR ASLPKDRSPE EYGITVISQP LNLTKEQLSE ITVLTTSVDA VVAICVIFS MSFVPASFVL YLIQERVNKS KHLQFISGVS PTTYWVTNFL WDIMNYSVSA GLVVGIFIGF QKKAYTSPEN L PALVALLL LYGWAVIPMM YPASFLFDVP STAYVALSCA NLFIGINSSA ITFILELFEN NRTLLRFNAV LRKLLIVFPH FC LGRGLID LALSQAVTDV YARFGEEHSA NPFHWDLIGK NLFAMVVEGV VYFLLTLLVQ RHFFLSQWIA EPTKEPIVDE DDD VAEERQ RIITGGNKTD ILRLHELTKI YPGTSSPAVD RLCVGVRPGE CFGLLGVNGA GKTTTFKMLT GDTTVTSGDA TVAG KSILT NISEVHQNMG YCPQFDAIDE LLTGREHLYL YARLRGVPAE EIEKVANWSI KSLGLTVYAD CLAGTYSGGN KRKLS TAIA LIGCPPLVLL DEPTTGMDPQ ARRMLWNVIV SIIREGRAVV LTSHSMEECE ALCTRLAIMV KGAFRCMGTI QHLKSK FGD GYIVTMKIKS PKDDLLPDLN PVEQFFQGNF PGSVQRERHY NMLQFQVSSS SLARIFQLLL SHKDSLLIEE YSVTQTT LD QVFVNFAKQQ TESHDLPLHP RAAGASRQAQ D UniProtKB: Retinal-specific phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA4 |
-Macromolecule #4: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2S)-3-[2-[(E)-[(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyc...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2S)-3-[2-[(E)-[(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenylidene]amino]ethoxy-oxidanyl-phosphoryl]oxy-2-[(Z)-octadec-9-enoyl]oxy-propyl] (Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: HZL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.010454 KDa |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HZL: |
-Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)