[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-22684: Cryo-EM structure of a chromatosome containing human linker histo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22684 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
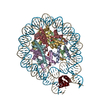
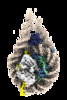
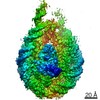
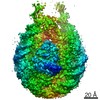
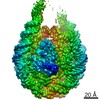
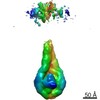
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | sharpened map of H1.4 chromatosome for structure model building | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | chromatosome / nucleosome / linker histones / Single-chain antibody / charge-charge interaction / chromatin / NUCLEAR PROTEIN / NUCLEAR PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of DNA recombination / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / chromosome condensation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus ...negative regulation of DNA recombination / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / chromosome condensation / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / heterochromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / nucleosomal DNA binding / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / telomere organization / Meiotic synapsis / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / innate immune response in mucosa / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / HDACs deacetylate histones / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / euchromatin / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / HDMs demethylate histones / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / chromatin DNA binding / heterochromatin formation / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / Metalloprotease DUBs / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / histone deacetylase binding / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / HCMV Early Events / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / chromatin organization / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / HATs acetylate histones / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / gene expression / double-stranded DNA binding / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / cadherin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  human (human) / human (human) /  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.76 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou B-R / Bai Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Distinct Structures and Dynamics of Chromatosomes with Different Human Linker Histone Isoforms. Authors: Bing-Rui Zhou / Hanqiao Feng / Seyit Kale / Tara Fox / Htet Khant / Natalia de Val / Rodolfo Ghirlando / Anna R Panchenko / Yawen Bai /    Abstract: The repeating structural unit of metazoan chromatin is the chromatosome, a nucleosome bound to a linker histone, H1. There are 11 human H1 isoforms with diverse cellular functions, but how they ...The repeating structural unit of metazoan chromatin is the chromatosome, a nucleosome bound to a linker histone, H1. There are 11 human H1 isoforms with diverse cellular functions, but how they interact with the nucleosome remains elusive. Here, we determined the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of chromatosomes containing 197 bp DNA and three different human H1 isoforms, respectively. The globular domains of all three H1 isoforms bound to the nucleosome dyad. However, the flanking/linker DNAs displayed substantial distinct dynamic conformations. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and H1 tail-swapping cryo-EM experiments revealed that the C-terminal tails of the H1 isoforms mainly controlled the flanking DNA orientations. We also observed partial ordering of the core histone H2A C-terminal and H3 N-terminal tails in the chromatosomes. Our results provide insights into the structures and dynamics of the chromatosomes and have implications for the structure and function of chromatin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22684.map.gz emd_22684.map.gz | 118.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22684-v30.xml emd-22684-v30.xml emd-22684.xml emd-22684.xml | 18.4 KB 18.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22684.png emd_22684.png | 116.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22684.cif.gz emd-22684.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22684 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22684 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_22684_validation.pdf.gz emd_22684_validation.pdf.gz | 508.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_22684_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_22684_full_validation.pdf.gz | 508.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_22684_validation.xml.gz emd_22684_validation.xml.gz | 6.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_22684_validation.cif.gz emd_22684_validation.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22684 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22684 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22684 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7k5yMC  7k5xC  7k60C  7k61C  7k63C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10574 (Title: Single-particle cryo-EM micrographs of a chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4 EMPIAR-10574 (Title: Single-particle cryo-EM micrographs of a chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4Data size: 208.9 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frames micrograph of a chomatosome containing human linker histone H1.4 [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22684.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22684.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
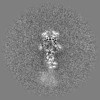
| Annotation | sharpened map of H1.4 chromatosome for structure model building | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.008 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4
| Entire | Name: chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4
| Supramolecule | Name: chromatosome containing human linker histone H1.4 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#8 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  human (human) human (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.437167 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK STGGKAPRKQ LATKAARKSA PATGGVKKPH RYRPGTVALR EIRRYQKSTE LLIRKLPFQR LVREIAQDFK TDLRFQSSA VMALQEACEA YLVGLFEDTN LCAIHAKRVT IMPKDIQLAR RIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.394426 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1-B/E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.165551 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK ARAKAKTRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY SERVGAGAPV YLAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAIR NDEELNKLLG RVTIAQGGVL PNIQAVLLPK KTESHHKAKG K UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1-B/E |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-J / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.935239 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAVT KAQKKDGKKR KRSRKESYSI YVYKVLKQVH PDTGISSKAM GIMNSFVNDI FERIAGEASR LAHYNKRST ITSREIQTAV RLLLPGELAK HAVSEGTKAV TKYTSAK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-J |
-Macromolecule #7: scFv20
| Macromolecule | Name: scFv20 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.34542 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKSSHHHHHH ENLYFQSNAM DIKMTQSPSS MHASLGERVT ITCKASQDIR SYLSWYQQKP WKSPKTLIYY ATSLADGVPS RFSGSGSGQ DFSLTINNLE SDDTATYYCL QHGESPYTFG SGTKLEIKRA GGGGSGGGGS GGGGSGGGGS MEVQLQQSGP E LVEPGTSV ...String: MKSSHHHHHH ENLYFQSNAM DIKMTQSPSS MHASLGERVT ITCKASQDIR SYLSWYQQKP WKSPKTLIYY ATSLADGVPS RFSGSGSGQ DFSLTINNLE SDDTATYYCL QHGESPYTFG SGTKLEIKRA GGGGSGGGGS GGGGSGGGGS MEVQLQQSGP E LVEPGTSV KMPCKASGYT FTSYTIQWVK QTPRQGLEWI GYIYPYNAGT KYNEKFKGKA TLTSDKSSST VYMELSSLTS ED SAVYYCA RKSSRLRSTL DYWGQGTSVT VSS |
-Macromolecule #8: Histone H1.4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H1.4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 21.931521 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSETAPAAPA APAPAEKTPV KKKARKSAGA AKRKASGPPV SELITKAVAA SKERSGVSLA ALKKALAAAG YDVEKNNSRI KLGLKSLVS KGTLVQTKGT GASGSFKLNK KAASGEAKPK AKKAGAAKAK KPAGAAKKPK KATGAATPKK SAKKTPKKAK K PAAAAGAK ...String: MSETAPAAPA APAPAEKTPV KKKARKSAGA AKRKASGPPV SELITKAVAA SKERSGVSLA ALKKALAAAG YDVEKNNSRI KLGLKSLVS KGTLVQTKGT GASGSFKLNK KAASGEAKPK AKKAGAAKAK KPAGAAKKPK KATGAATPKK SAKKTPKKAK K PAAAAGAK KAKSPKKAKA AKPKKAPKSP AKAKAVKPKA AKPKTAKPKA AKPKKAAAKK K UniProtKB: Histone H1.4 |
-Macromolecule #5: DNA (197-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (197-MER) / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.510484 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DT) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG) ...String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DT) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DT) (DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC) |
-Macromolecule #6: DNA (197-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (197-MER) / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.141883 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) ...String: (DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA) (DT) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DG) (DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DA) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG) (DC) (DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: Details: input pdb models: 4QLC, 6DZT, 5NL0 5Y0C |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.76 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. 2) / Number images used: 112385 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)