+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | IstA-IstB(E167Q) Strand Transfer Complex | |||||||||
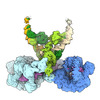
 Map data Map data | sharpened map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA transposition / DNA integration / transposon / transpososome / holo-transpososome / insertion sequence / IS21 / IstA / IstB / DDE transposase / DDE domain / AAA+ ATPase / DNA strand transfer complex / STC / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtransposition / DNA strand exchange activity / DNA integration / DNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) | |||||||||
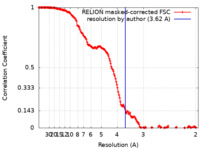
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.62 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | de la Gandara A / Spinola-Amilibia M / Araujo-Bazan L / Nunez-Ramirez R / Berger JM / Arias-Palomo E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Spain, 2 items Spain, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Molecular basis for transposase activation by a dedicated AAA+ ATPase. Authors: Álvaro de la Gándara / Mercedes Spínola-Amilibia / Lidia Araújo-Bazán / Rafael Núñez-Ramírez / James M Berger / Ernesto Arias-Palomo /   Abstract: Transposases drive chromosomal rearrangements and the dissemination of drug-resistance genes and toxins. Although some transposases act alone, many rely on dedicated AAA+ ATPase subunits that ...Transposases drive chromosomal rearrangements and the dissemination of drug-resistance genes and toxins. Although some transposases act alone, many rely on dedicated AAA+ ATPase subunits that regulate site selectivity and catalytic function through poorly understood mechanisms. Using IS21 as a model transposase system, we show how an ATPase regulator uses nucleotide-controlled assembly and DNA deformation to enable structure-based site selectivity, transposase recruitment, and activation and integration. Solution and cryogenic electron microscopy studies show that the IstB ATPase self-assembles into an autoinhibited pentamer of dimers that tightly curves target DNA into a half-coil. Two of these decamers dimerize, which stabilizes the target nucleic acid into a kinked S-shaped configuration that engages the IstA transposase at the interface between the two IstB oligomers to form an approximately 1 MDa transpososome complex. Specific interactions stimulate regulator ATPase activity and trigger a large conformational change on the transposase that positions the catalytic site to perform DNA strand transfer. These studies help explain how AAA+ ATPase regulators-which are used by classical transposition systems such as Tn7, Mu and CRISPR-associated elements-can remodel their substrate DNA and cognate transposases to promote function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18144.map.gz emd_18144.map.gz | 347.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18144-v30.xml emd-18144-v30.xml emd-18144.xml emd-18144.xml | 31.3 KB 31.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18144_fsc.xml emd_18144_fsc.xml | 16.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18144.png emd_18144.png | 136.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_18144_msk_1.map emd_18144_msk_1.map | 371.3 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18144.cif.gz emd-18144.cif.gz | 7.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18144_additional_1.map.gz emd_18144_additional_1.map.gz emd_18144_additional_2.map.gz emd_18144_additional_2.map.gz emd_18144_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18144_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18144_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18144_half_map_2.map.gz | 347.3 MB 295 MB 294.9 MB 294.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18144 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18144 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18144 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18144 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_18144_validation.pdf.gz emd_18144_validation.pdf.gz | 957.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_18144_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_18144_full_validation.pdf.gz | 957.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_18144_validation.xml.gz emd_18144_validation.xml.gz | 23.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_18144_validation.cif.gz emd_18144_validation.cif.gz | 31.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18144 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18144 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18144 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-18144 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8q4dMC  18136 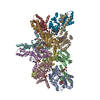 8q3wC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18144.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 371.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18144.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 371.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.98498 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_18144_msk_1.map emd_18144_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : IstA-IstB(E167Q) Strand Transfer Complex
+Supramolecule #1: IstA-IstB(E167Q) Strand Transfer Complex
+Supramolecule #2: IstA-IstB(E167Q) Strand
+Supramolecule #3: DNA
+Macromolecule #1: Putative transposase for insertion sequence element IS5376
+Macromolecule #2: Insertion sequence IS5376 putative ATP-binding protein
+Macromolecule #3: DNA (118-MER) / TIR-transferred strand
+Macromolecule #4: DNA (58-MER) / TIR non-transferred strand
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (58-MER) / target-reverse complement
+Macromolecule #6: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #8: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 2.1 sec. / Average electron dose: 51.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 91.21 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8q4d: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z
Z Y
Y X
X