+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1702 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
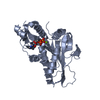
| Title | Kif18A (ATP state) head bound to a microtubule | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 15 protofilament microtubule decorated with the motor domain of Kif18A complexed with AMPPNP | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Molecular motor / kinesin 8 / ruby-helix | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 13.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Peters C / Brejc K / Belmont L / Bodey A / Lee Y / Yu M / Ramchandani S / Guo J / Lichtsteiner S / Wood KW ...Peters C / Brejc K / Belmont L / Bodey A / Lee Y / Yu M / Ramchandani S / Guo J / Lichtsteiner S / Wood KW / Sakowicz R / Hartman J / Moores C | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2010 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2010Title: Insight into the molecular mechanism of the multitasking kinesin-8 motor. Authors: Carsten Peters / Katjuša Brejc / Lisa Belmont / Andrew J Bodey / Yan Lee / Ming Yu / Jun Guo / Roman Sakowicz / James Hartman / Carolyn A Moores /  Abstract: Members of the kinesin-8 motor class have the remarkable ability to both walk towards microtubule plus-ends and depolymerise these ends on arrival, thereby regulating microtubule length. To analyse ...Members of the kinesin-8 motor class have the remarkable ability to both walk towards microtubule plus-ends and depolymerise these ends on arrival, thereby regulating microtubule length. To analyse how kinesin-8 multitasks, we studied the structure and function of the kinesin-8 motor domain. We determined the first crystal structure of a kinesin-8 and used cryo-electron microscopy to calculate the structure of the microtubule-bound motor. Microtubule-bound kinesin-8 reveals a new conformation compared with the crystal structure, including a bent conformation of the α4 relay helix and ordering of functionally important loops. The kinesin-8 motor domain does not depolymerise stabilised microtubules with ATP but does form tubulin rings in the presence of a non-hydrolysable ATP analogue. This shows that, by collaborating, kinesin-8 motor domain molecules can release tubulin from microtubules, and that they have a similar mechanical effect on microtubule ends as kinesin-13, which enables depolymerisation. Our data reveal aspects of the molecular mechanism of kinesin-8 motors that contribute to their unique dual motile and depolymerising functions, which are adapted to control microtubule length. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1702.map.gz emd_1702.map.gz | 107.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1702-v30.xml emd-1702-v30.xml emd-1702.xml emd-1702.xml | 10.8 KB 10.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  4db-AMPPNP_500.tif 4db-AMPPNP_500.tif | 732.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1702 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1702 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_1702_validation.pdf.gz emd_1702_validation.pdf.gz | 295.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_1702_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_1702_full_validation.pdf.gz | 294.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_1702_validation.xml.gz emd_1702_validation.xml.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1702 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-1702 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1702.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 122.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1702.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 122.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 15 protofilament microtubule decorated with the motor domain of Kif18A complexed with AMPPNP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
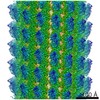
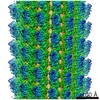
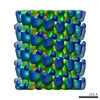
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Microtubule complexed with motor domain of Kif18A (ATP state)
| Entire | Name: Microtubule complexed with motor domain of Kif18A (ATP state) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Microtubule complexed with motor domain of Kif18A (ATP state)
| Supramolecule | Name: Microtubule complexed with motor domain of Kif18A (ATP state) type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 3 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Motor domain of Kif18A
| Macromolecule | Name: Motor domain of Kif18A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Motor domain of Kif18A / Details: Contains the N-terminal 355 aa / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: Cytoplasm Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: Cytoplasm |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Escherichia coli Rosetta DE3 |
-Macromolecule #2: Beta tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: Beta tubulin / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #3: Alpha tubulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Alpha tubulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: Alpha tubulin / Recombinant expression: No / Database: NCBI |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 Details: 80mM PIPES, 150mM NaCl, 7mM MgCl2, 1mM EGTA, 1mM beta-mercaptoethanol |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 400 mesh copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Details: Vitrification instrument: Manual plunger / Timed resolved state: Sample contained 2mM AMPPNP / Method: Blotted for 1 sec before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lense stigmatism was corrected at 150,000 times magnification |
| Details | Low dose |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: ZEISS SCAI / Digitization - Sampling interval: 7 µm / Number real images: 21 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 12 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.82 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.74 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Cryo-holder / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 13.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Ruby-Helix Details: Fourier Bessel Synthesis using data from 24 microtubules (32000 asymmetric units) |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Phase flipping, Wiener |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















