+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
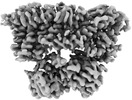
| Title | Structure of the K+/H+ exchanger KefC with GSH | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | potassium proton exchanger / KefC / Transporter / CPA / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / GSH | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglutathione-regulated potassium exporter activity / response to methylglyoxal / potassium:proton antiporter complex / intracellular pH elevation / regulation of pH / toxic substance binding / proton transmembrane transport / regulation of intracellular pH / potassium ion transport / response to hydrogen peroxide ...glutathione-regulated potassium exporter activity / response to methylglyoxal / potassium:proton antiporter complex / intracellular pH elevation / regulation of pH / toxic substance binding / proton transmembrane transport / regulation of intracellular pH / potassium ion transport / response to hydrogen peroxide / response to toxic substance / nucleotide binding / enzyme binding / protein homodimerization activity / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
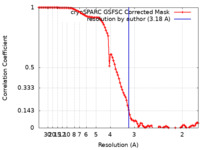
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.18 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gulati A / Drew D | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Sweden, 2 items Sweden, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structure and mechanism of the K/H exchanger KefC. Authors: Ashutosh Gulati / Surabhi Kokane / Annemarie Perez-Boerema / Claudia Alleva / Pascal F Meier / Rei Matsuoka / David Drew /  Abstract: Intracellular potassium (K) homeostasis is fundamental to cell viability. In addition to channels, K levels are maintained by various ion transporters. One major family is the proton-driven K efflux ...Intracellular potassium (K) homeostasis is fundamental to cell viability. In addition to channels, K levels are maintained by various ion transporters. One major family is the proton-driven K efflux transporters, which in gram-negative bacteria is important for detoxification and in plants is critical for efficient photosynthesis and growth. Despite their importance, the structure and molecular basis for K-selectivity is poorly understood. Here, we report ~3.1 Å resolution cryo-EM structures of the Escherichia coli glutathione (GSH)-gated K efflux transporter KefC in complex with AMP, AMP/GSH and an ion-binding variant. KefC forms a homodimer similar to the inward-facing conformation of Na/H antiporter NapA. By structural assignment of a coordinated K ion, MD simulations, and SSM-based electrophysiology, we demonstrate how ion-binding in KefC is adapted for binding a dehydrated K ion. KefC harbors C-terminal regulator of K conductance (RCK) domains, as present in some bacterial K-ion channels. The domain-swapped helices in the RCK domains bind AMP and GSH and they inhibit transport by directly interacting with the ion-transporter module. Taken together, we propose that KefC is activated by detachment of the RCK domains and that ion selectivity exploits the biophysical properties likewise adapted by K-ion-channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_16319.map.gz emd_16319.map.gz | 95.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-16319-v30.xml emd-16319-v30.xml emd-16319.xml emd-16319.xml | 15.4 KB 15.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_16319_fsc.xml emd_16319_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
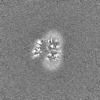
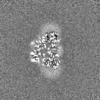
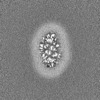
| Images |  emd_16319.png emd_16319.png | 96.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-16319.cif.gz emd-16319.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_16319_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16319_half_map_1.map.gz emd_16319_half_map_2.map.gz emd_16319_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.5 MB 95.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16319 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-16319 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8by2MC  8bxgC  9embC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_16319.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_16319.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
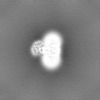
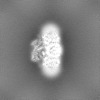
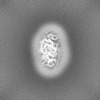
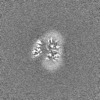
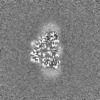
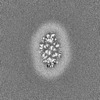
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.886 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
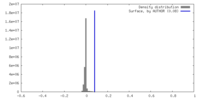
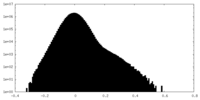
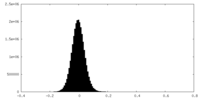
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_16319_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
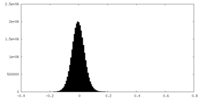
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_16319_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Kefc protein dimer with GSH
| Entire | Name: Kefc protein dimer with GSH |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Kefc protein dimer with GSH
| Supramolecule | Name: Kefc protein dimer with GSH / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutathione-regulated potassium-efflux system protein KefC
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutathione-regulated potassium-efflux system protein KefC type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.183223 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDSHTLIQAL IYLGSAALIV PIAVRLGLGS VLGYLIAGCI IGPWGLRLVT DAESILHFAE IGVVLMLFII GLELDPQRLW KLRAAVFGG GALQMVICGG LLGLFCMLLG LRWQVAELIG MTLALSSTAI AMQAMNERNL MVTQMGRSAF AVLLFQDIAA I PLVAMIPL ...String: MDSHTLIQAL IYLGSAALIV PIAVRLGLGS VLGYLIAGCI IGPWGLRLVT DAESILHFAE IGVVLMLFII GLELDPQRLW KLRAAVFGG GALQMVICGG LLGLFCMLLG LRWQVAELIG MTLALSSTAI AMQAMNERNL MVTQMGRSAF AVLLFQDIAA I PLVAMIPL LATSSASTTM GAFALSALKV AGALVLVVLL GRYVTRPALR FVARSGLREV FSAVALFLVF GFGLLLEEVG LS MAMGAFL AGVLLASSEY RHALESDIEP FKGLLLGLFF IGVGMSIDFG TLLENPLRIV ILLLGFLIIK IAMLWLIARP LQV PNKQRR WFAVLLGQGS EFAFVVFGAA QMANVLEPEW AKSLTLAVAL SMAATPILLV ILNRLEQSST EEAREADEID EEQP RVIIA GFGRFGQITG RLLLSSGVKM VVLDHDPDHI ETLRKFGMKV FYGDATRMDL LESAGAAKAE VLINAIDDPQ TNLQL TEMV KEHFPHLQII ARARDVDHYI RLRQAGVEKP ERETFEGALK TGRLALESLG LGPYEARERA DVFRRFNIQM VEEMAM V UniProtKB: Glutathione-regulated potassium-efflux system protein KefC |
-Macromolecule #2: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: AMP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 347.221 Da |
| Chemical component information | 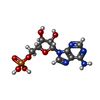 ChemComp-AMP: |
-Macromolecule #4: GLUTATHIONE
| Macromolecule | Name: GLUTATHIONE / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: GSH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 307.323 Da |
| Chemical component information | 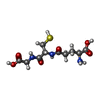 ChemComp-GSH: |
-Macromolecule #5: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]o...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1R)-2-{[(S)-{[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]oxy}(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-1-[(hexadecanoyloxy)methyl]ethyl (9Z)-octadec-9-enoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PGW |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 749.007 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 64.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) X (Row.)
X (Row.) Y (Col.)
Y (Col.)