+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8by2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
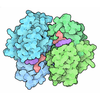
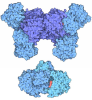
| Title | Structure of the K+/H+ exchanger KefC with GSH. | |||||||||
 Components Components | Glutathione-regulated potassium-efflux system protein KefC | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / potassium proton exchanger / KefC / Transporter / CPA / GSH | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglutathione-regulated potassium exporter activity / response to methylglyoxal / potassium:proton antiporter complex / intracellular pH elevation / regulation of pH / toxic substance binding / proton transmembrane transport / regulation of intracellular pH / potassium ion transport / response to hydrogen peroxide ...glutathione-regulated potassium exporter activity / response to methylglyoxal / potassium:proton antiporter complex / intracellular pH elevation / regulation of pH / toxic substance binding / proton transmembrane transport / regulation of intracellular pH / potassium ion transport / response to hydrogen peroxide / response to toxic substance / nucleotide binding / enzyme binding / protein homodimerization activity / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.18 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gulati, A. / Drew, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Sweden, 2items Sweden, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Structure and mechanism of the K/H exchanger KefC. Authors: Ashutosh Gulati / Surabhi Kokane / Annemarie Perez-Boerema / Claudia Alleva / Pascal F Meier / Rei Matsuoka / David Drew /  Abstract: Intracellular potassium (K) homeostasis is fundamental to cell viability. In addition to channels, K levels are maintained by various ion transporters. One major family is the proton-driven K efflux ...Intracellular potassium (K) homeostasis is fundamental to cell viability. In addition to channels, K levels are maintained by various ion transporters. One major family is the proton-driven K efflux transporters, which in gram-negative bacteria is important for detoxification and in plants is critical for efficient photosynthesis and growth. Despite their importance, the structure and molecular basis for K-selectivity is poorly understood. Here, we report ~3.1 Å resolution cryo-EM structures of the Escherichia coli glutathione (GSH)-gated K efflux transporter KefC in complex with AMP, AMP/GSH and an ion-binding variant. KefC forms a homodimer similar to the inward-facing conformation of Na/H antiporter NapA. By structural assignment of a coordinated K ion, MD simulations, and SSM-based electrophysiology, we demonstrate how ion-binding in KefC is adapted for binding a dehydrated K ion. KefC harbors C-terminal regulator of K conductance (RCK) domains, as present in some bacterial K-ion channels. The domain-swapped helices in the RCK domains bind AMP and GSH and they inhibit transport by directly interacting with the ion-transporter module. Taken together, we propose that KefC is activated by detachment of the RCK domains and that ion selectivity exploits the biophysical properties likewise adapted by K-ion-channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8by2.cif.gz 8by2.cif.gz | 520.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8by2.ent.gz pdb8by2.ent.gz | 346 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8by2.json.gz 8by2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/by/8by2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/by/8by2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/by/8by2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/by/8by2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16319MC  8bxgC  9embC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 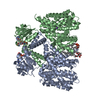
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 61183.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | #5: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Kefc protein dimer with GSH / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.18 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 260115 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 82.62 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj