+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
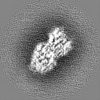
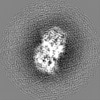
| Title | D. melanogaster alpha/beta tubulin heterodimer in the GTP form | |||||||||
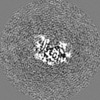
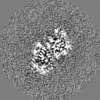
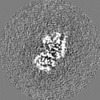
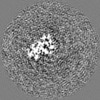
 Map data Map data | alpha/beta tubulin heterdimer from D. melanogaster in the GTP form | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cytyoskeleton / microtubules / cytomotive filaments / CELL CYCLE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Kinesins / astral microtubule / Neutrophil degranulation / lysosome localization / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton ...HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Kinesins / astral microtubule / Neutrophil degranulation / lysosome localization / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / mitotic cell cycle / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / centrosome / GTP binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / nucleus / metal ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
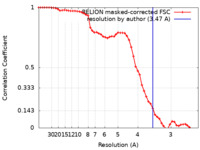
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.47 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wagstaff J / Planelles-Herrero VJ / Derivery E / Lowe J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Diverse cytomotive actins and tubulins share a polymerization switch mechanism conferring robust dynamics. Authors: James Mark Wagstaff / Vicente José Planelles-Herrero / Grigory Sharov / Aisha Alnami / Frank Kozielski / Emmanuel Derivery / Jan Löwe /  Abstract: Protein filaments are used in myriads of ways to organize other molecules within cells. Some filament-forming proteins couple the hydrolysis of nucleotides to their polymerization cycle, thus ...Protein filaments are used in myriads of ways to organize other molecules within cells. Some filament-forming proteins couple the hydrolysis of nucleotides to their polymerization cycle, thus powering the movement of other molecules. These filaments are termed cytomotive. Only members of the actin and tubulin protein superfamilies are known to form cytomotive filaments. We examined the basis of cytomotivity via structural studies of the polymerization cycles of actin and tubulin homologs from across the tree of life. We analyzed published data and performed structural experiments designed to disentangle functional components of these complex filament systems. Our analysis demonstrates the existence of shared subunit polymerization switches among both cytomotive actins and tubulins, i.e., the conformation of subunits switches upon assembly into filaments. These cytomotive switches can explain filament robustness, by enabling the coupling of kinetic and structural polarities required for cytomotive behaviors and by ensuring that single cytomotive filaments do not fall apart. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14148.map.gz emd_14148.map.gz | 92.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14148-v30.xml emd-14148-v30.xml emd-14148.xml emd-14148.xml | 14.3 KB 14.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_14148_fsc.xml emd_14148_fsc.xml | 5.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_14148.png emd_14148.png | 99.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14148.cif.gz emd-14148.cif.gz | 6.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14148 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14148 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14148 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14148 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_14148_validation.pdf.gz emd_14148_validation.pdf.gz | 615.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_14148_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_14148_full_validation.pdf.gz | 615.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_14148_validation.xml.gz emd_14148_validation.xml.gz | 9.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_14148_validation.cif.gz emd_14148_validation.cif.gz | 11.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14148 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14148 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14148 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14148 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7qudMC  7qucC  7qupC  7quqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14148.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 98.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14148.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 98.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | alpha/beta tubulin heterdimer from D. melanogaster in the GTP form | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.622 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
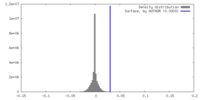
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : alpha1/beta tubulin heterodimer
| Entire | Name: alpha1/beta tubulin heterodimer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: alpha1/beta tubulin heterodimer
| Supramolecule | Name: alpha1/beta tubulin heterodimer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1 chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1 chain / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Tubulin beta-1 chain
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin beta-1 chain / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin alpha-1 chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1 chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.772324 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHEDQ VDPRLIDGKG GGGRPMRECI SIHVGQAGVQ IGNACWELYC LEHGIQPDGQ MPSDKTVGGG DDSFNTFFSE TGAGKHVPR AVFVDLEPTV VDEVRTGTYR QLFHPEQLIT GKEDAANNYA RGHYTIGKEI VDLVLDRIRK LADQCTGLQG F LIFHSFGG ...String: MHHHHHHEDQ VDPRLIDGKG GGGRPMRECI SIHVGQAGVQ IGNACWELYC LEHGIQPDGQ MPSDKTVGGG DDSFNTFFSE TGAGKHVPR AVFVDLEPTV VDEVRTGTYR QLFHPEQLIT GKEDAANNYA RGHYTIGKEI VDLVLDRIRK LADQCTGLQG F LIFHSFGG GTGSGFTSLL MERLSVDYGK KSKLEFAIYP APQVSTAVVE PYNSILTTHT TLEHSDCAFM VDNEAIYDIC RR NLDIERP TYTNLNRLIG QIVSSITASL RFDGALNVDL TEFQTNLVPY PRIHFPLVTY APVISAEKAY HEQLSVAEIT NAC FEPANQ MVKCDPRHGK YMACCMLYRG DVVPKDVNAA IATIKTKRTI QFVDWCPTGF KVGINYQPPT VVPGGDLAKV QRAV CMLSN TTAIAEAWAR LDHKFDLMYA KRAFVHWYVG EGMEEGEFSE AREDLAALEK DYEEVGMDSG DGEGEGAEEY UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1 chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin beta-1 chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta-1 chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50.194137 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEIISDEHGI DATGAYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEASGGKYV PRAVLVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTYS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEIISDEHGI DATGAYHGDS DLQLERINVY YNEASGGKYV PRAVLVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTYS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSLTMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQMFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAIF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNIQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMSAT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY QEATADEDAE FEEEQEAEVD EN UniProtKB: Tubulin beta-1 chain |
-Macromolecule #3: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6.9 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 4037 / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)