+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7qup | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
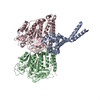
| Title | D. melanogaster 13-protofilament microtubule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / Cytyoskeleton / microtubules / cytomotive filaments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Kinesins / Neutrophil degranulation / astral microtubule / lysosome localization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization ...HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / Kinesins / Neutrophil degranulation / astral microtubule / lysosome localization / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / spindle / mitotic cell cycle / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / microtubule / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / centrosome / GTP binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wagstaff, J. / Planelles-Herrero, V.J. / Derivery, E. / Lowe, J. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Diverse cytomotive actins and tubulins share a polymerization switch mechanism conferring robust dynamics. Authors: James Mark Wagstaff / Vicente José Planelles-Herrero / Grigory Sharov / Aisha Alnami / Frank Kozielski / Emmanuel Derivery / Jan Löwe /  Abstract: Protein filaments are used in myriads of ways to organize other molecules within cells. Some filament-forming proteins couple the hydrolysis of nucleotides to their polymerization cycle, thus ...Protein filaments are used in myriads of ways to organize other molecules within cells. Some filament-forming proteins couple the hydrolysis of nucleotides to their polymerization cycle, thus powering the movement of other molecules. These filaments are termed cytomotive. Only members of the actin and tubulin protein superfamilies are known to form cytomotive filaments. We examined the basis of cytomotivity via structural studies of the polymerization cycles of actin and tubulin homologs from across the tree of life. We analyzed published data and performed structural experiments designed to disentangle functional components of these complex filament systems. Our analysis demonstrates the existence of shared subunit polymerization switches among both cytomotive actins and tubulins, i.e., the conformation of subunits switches upon assembly into filaments. These cytomotive switches can explain filament robustness, by enabling the coupling of kinetic and structural polarities required for cytomotive behaviors and by ensuring that single cytomotive filaments do not fall apart. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7qup.cif.gz 7qup.cif.gz | 4.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7qup.ent.gz pdb7qup.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7qup.json.gz 7qup.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/7qup https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/7qup ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/7qup ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/7qup | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  14150MC  7qucC  7qudC  7quqC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52772.324 Da / Num. of mol.: 39 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 47681.707 Da / Num. of mol.: 26 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Microtubule / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.170 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.9 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 32 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: UCSF ChimeraX / Version: 1.4/v9 / Classification: model building / URL: https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ / Os: macOS / Type: package |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 39594 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION Details: Resolution was determined against the atomic model, suing FSC 0.5 Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 3J1T Accession code: 3J1T / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj