+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13292 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the MoStoNano fusion protein | ||||||||||||
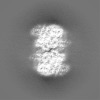
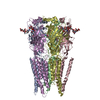
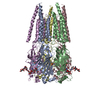
 Map data Map data | The structure of MoStoNano | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnutrient reservoir activity / molybdenum ion binding / protein-disulfide reductase activity / cell redox homeostasis / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
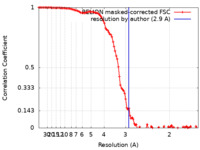
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Benoit RM / Poghosyan E | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 3 items Switzerland, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2022 Journal: Structure / Year: 2022Title: Chimeric single α-helical domains as rigid fusion protein connections for protein nanotechnology and structural biology. Authors: Gabriella Collu / Tobias Bierig / Anna-Sophia Krebs / Sylvain Engilberge / Niveditha Varma / Ramon Guixà-González / Timothy Sharpe / Xavier Deupi / Vincent Olieric / Emiliya Poghosyan / Roger M Benoit /  Abstract: Chimeric fusion proteins are essential tools for protein nanotechnology. Non-optimized protein-protein connections are usually flexible and therefore unsuitable as structural building blocks. Here we ...Chimeric fusion proteins are essential tools for protein nanotechnology. Non-optimized protein-protein connections are usually flexible and therefore unsuitable as structural building blocks. Here we show that the ER/K motif, a single α-helical domain (SAH), can be seamlessly fused to terminal helices of proteins, forming an extended, partially free-standing rigid helix. This enables the connection of two domains at a defined distance and orientation. We designed three constructs termed YFPnano, T4Lnano, and MoStoNano. Analysis of experimentally determined structures and molecular dynamics simulations reveals a certain degree of plasticity in the connections that allows the adaptation to crystal contact opportunities. Our data show that SAHs can be stably integrated into designed structural elements, enabling new possibilities for protein nanotechnology, for example, to improve the exposure of epitopes on nanoparticles (structural vaccinology), to engineer crystal contacts with minimal impact on construct flexibility (for the study of protein dynamics), and to design novel biomaterials. #1:  Journal: To Be Published Journal: To Be PublishedTitle: Chimeric single alpha-helical domains as rigid fusion protein connections for protein nanotechnology and structural biology Authors: Benoit RM / Poghosyan E | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13292.map.gz emd_13292.map.gz | 96.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13292-v30.xml emd-13292-v30.xml emd-13292.xml emd-13292.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13292_fsc.xml emd_13292_fsc.xml | 10.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13292.png emd_13292.png | 90.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13292_msk_1.map emd_13292_msk_1.map | 103 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_13292_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13292_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13292_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13292_half_map_2.map.gz | 80.8 MB 80.8 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13292 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13292 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13292 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13292 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13292_validation.pdf.gz emd_13292_validation.pdf.gz | 568 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13292_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13292_full_validation.pdf.gz | 567.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13292_validation.xml.gz emd_13292_validation.xml.gz | 17.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13292_validation.cif.gz emd_13292_validation.cif.gz | 23 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13292 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13292 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13292 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13292 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13292.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13292.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The structure of MoStoNano | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
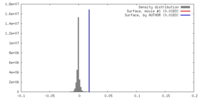
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
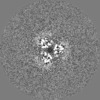
| File |  emd_13292_msk_1.map emd_13292_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
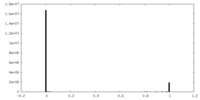
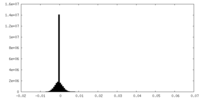
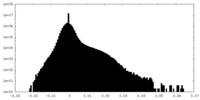
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map after the refinement
| File | emd_13292_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map after the refinement | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
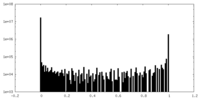
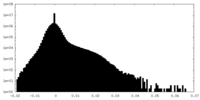
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map after the refinement
| File | emd_13292_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map after the refinement | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : MoStoNano fusion protein
| Entire | Name: MoStoNano fusion protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: MoStoNano fusion protein
| Supramolecule | Name: MoStoNano fusion protein / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.4 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.5 |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | The sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3710 pixel / Number real images: 2472 / Average electron dose: 62.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 165000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)