+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13218 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Progressive supranuclear palsy tau filament | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Amyloid fibril / PROTEIN FIBRIL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding / tubulin complex ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / axonal transport / histone-dependent DNA binding / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of diacylglycerol kinase activity / negative regulation of establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / microtubule lateral binding / tubulin complex / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / main axon / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / negative regulation of kinase activity / negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation / generation of neurons / regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of protein localization / rRNA metabolic process / internal protein amino acid acetylation / regulation of mitochondrial fission / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / axonal transport of mitochondrion / axon development / central nervous system neuron development / regulation of microtubule polymerization / microtubule polymerization / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / lipoprotein particle binding / dynactin binding / apolipoprotein binding / glial cell projection / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / protein polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / axolemma / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / positive regulation of axon extension / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / supramolecular fiber organization / regulation of cellular response to heat / stress granule assembly / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / axon cytoplasm / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / somatodendritic compartment / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / synapse assembly / phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / protein phosphatase 2A binding / regulation of autophagy / astrocyte activation / response to lead ion / synapse organization / microglial cell activation / Hsp90 protein binding / regulation of synaptic plasticity / PKR-mediated signaling / protein homooligomerization / memory / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / SH3 domain binding / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process / neuron projection development / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell-cell signaling / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / actin binding / single-stranded DNA binding / cellular response to heat / protein-folding chaperone binding / cell body / growth cone / microtubule binding / double-stranded DNA binding / microtubule / amyloid fibril formation / sequence-specific DNA binding / dendritic spine / learning or memory / nuclear speck / neuron projection / membrane raft / axon / negative regulation of gene expression / neuronal cell body / DNA damage response / dendrite / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
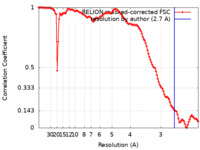
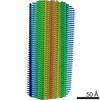
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shi Y / Zhang W | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, United Kingdom, European Union,  Japan, Japan,  United States, 12 items United States, 12 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structure-based classification of tauopathies. Authors: Yang Shi / Wenjuan Zhang / Yang Yang / Alexey G Murzin / Benjamin Falcon / Abhay Kotecha / Mike van Beers / Airi Tarutani / Fuyuki Kametani / Holly J Garringer / Ruben Vidal / Grace I ...Authors: Yang Shi / Wenjuan Zhang / Yang Yang / Alexey G Murzin / Benjamin Falcon / Abhay Kotecha / Mike van Beers / Airi Tarutani / Fuyuki Kametani / Holly J Garringer / Ruben Vidal / Grace I Hallinan / Tammaryn Lashley / Yuko Saito / Shigeo Murayama / Mari Yoshida / Hidetomo Tanaka / Akiyoshi Kakita / Takeshi Ikeuchi / Andrew C Robinson / David M A Mann / Gabor G Kovacs / Tamas Revesz / Bernardino Ghetti / Masato Hasegawa / Michel Goedert / Sjors H W Scheres /       Abstract: The ordered assembly of tau protein into filaments characterizes several neurodegenerative diseases, which are called tauopathies. It was previously reported that, by cryo-electron microscopy, the ...The ordered assembly of tau protein into filaments characterizes several neurodegenerative diseases, which are called tauopathies. It was previously reported that, by cryo-electron microscopy, the structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, chronic traumatic encephalopathy and corticobasal degeneration are distinct. Here we show that the structures of tau filaments from progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) define a new three-layered fold. Moreover, the structures of tau filaments from globular glial tauopathy are similar to those from PSP. The tau filament fold of argyrophilic grain disease (AGD) differs, instead resembling the four-layered fold of corticobasal degeneration. The AGD fold is also observed in ageing-related tau astrogliopathy. Tau protofilament structures from inherited cases of mutations at positions +3 or +16 in intron 10 of MAPT (the microtubule-associated protein tau gene) are also identical to those from AGD, suggesting that relative overproduction of four-repeat tau can give rise to the AGD fold. Finally, the structures of tau filaments from cases of familial British dementia and familial Danish dementia are the same as those from cases of Alzheimer's disease and primary age-related tauopathy. These findings suggest a hierarchical classification of tauopathies on the basis of their filament folds, which complements clinical diagnosis and neuropathology and also allows the identification of new entities-as we show for a case diagnosed as PSP, but with filament structures that are intermediate between those of globular glial tauopathy and PSP. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13218.map.gz emd_13218.map.gz | 23.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13218-v30.xml emd-13218-v30.xml emd-13218.xml emd-13218.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13218_fsc.xml emd_13218_fsc.xml | 12 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13218.png emd_13218.png | 118.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13218_msk_1.map emd_13218_msk_1.map | 149.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13218.cif.gz emd-13218.cif.gz | 5.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13218_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13218_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13218_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13218_half_map_2.map.gz | 118.4 MB 118.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13218 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13218 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13218 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13218 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_13218_validation.pdf.gz emd_13218_validation.pdf.gz | 906.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_13218_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_13218_full_validation.pdf.gz | 905.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_13218_validation.xml.gz emd_13218_validation.xml.gz | 19.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_13218_validation.cif.gz emd_13218_validation.cif.gz | 25.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13218 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13218 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13218 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-13218 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7p65MC  7p66C  7p67C  7p68C  7p6aC  7p6bC  7p6cC  7p6dC  7p6eC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10765 (Title: Single particle cryo-EM dataset of sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individual with progressive supranuclear palsy EMPIAR-10765 (Title: Single particle cryo-EM dataset of sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individual with progressive supranuclear palsyData size: 967.4 Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame movies [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13218.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13218.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.15 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
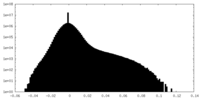
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13218_msk_1.map emd_13218_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_13218_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_13218_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individ...
| Entire | Name: Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individual with progressive supranuclear palsy |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individ...
| Supramolecule | Name: Sarkosyl-insoluble fraction from the frontal cortex of an individual with progressive supranuclear palsy type: tissue / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Microtubule-associated protein tau
| Macromolecule | Name: Microtubule-associated protein tau / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.919871 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAEPRQEFEV MEDHAGTYGL GDRKDQGGYT MHQDQEGDTD AGLKESPLQT PTEDGSEEPG SETSDAKSTP TAEDVTAPLV DEGAPGKQA AAQPHTEIPE GTTAEEAGIG DTPSLEDEAA GHVTQARMVS KSKDGTGSDD KKAKGADGKT KIATPRGAAP P GQKGQANA ...String: MAEPRQEFEV MEDHAGTYGL GDRKDQGGYT MHQDQEGDTD AGLKESPLQT PTEDGSEEPG SETSDAKSTP TAEDVTAPLV DEGAPGKQA AAQPHTEIPE GTTAEEAGIG DTPSLEDEAA GHVTQARMVS KSKDGTGSDD KKAKGADGKT KIATPRGAAP P GQKGQANA TRIPAKTPPA PKTPPSSGEP PKSGDRSGYS SPGSPGTPGS RSRTPSLPTP PTREPKKVAV VRTPPKSPSS AK SRLQTAP VPMPDLKNVK SKIGSTENLK HQPGGGKVQI INKKLDLSNV QSKCGSKDNI KHVPGGGSVQ IVYKPVDLSK VTS KCGSLG NIHHKPGGGQ VEVKSEKLDF KDRVQSKIGS LDNITHVPGG GNKKIETHKL TFRENAKAKT DHGAEIVYKS PVVS GDTSP RHLSNVSSTG SIDMVDSPQL ATLADEVSAS LAKQGL UniProtKB: Microtubule-associated protein tau |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | helical array |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z
Z Y
Y X
X