[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8uhg: Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II-DSIF-NELF - pois... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uhg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
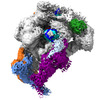
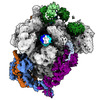
| Title | Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II-DSIF-NELF - poised post-translocated | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA/RNA /  Nucleic acids / Nucleic acids /  transcription / transcription /  RNA polymerase II / NELF / RNA polymerase II / NELF /  DSIF / pausing / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA-RNA complex DSIF / pausing / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA-RNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationNELF complex / positive regulation of protein modification process / NTRK3 as a dependence receptor / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation /  DSIF complex / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape ...NELF complex / positive regulation of protein modification process / NTRK3 as a dependence receptor / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / DSIF complex / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape ...NELF complex / positive regulation of protein modification process / NTRK3 as a dependence receptor / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation /  DSIF complex / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / negative regulation of stem cell differentiation / nuclear lumen / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling / DSIF complex / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / nuclear DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / negative regulation of stem cell differentiation / nuclear lumen / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / transcription elongation-coupled chromatin remodeling /  RNA polymerase complex / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / RNA polymerase complex / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery /  RNA polymerase II activity / organelle membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / RNA polymerase II activity / organelle membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat /  RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase I complex /  RNA polymerase III complex / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / localization / RNA polymerase III complex / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / localization /  RNA polymerase II, core complex / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / RNA polymerase II, core complex / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex /  stem cell differentiation / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / stem cell differentiation / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II /  transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / DNA-templated transcription initiation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / DNA-templated transcription initiation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes /  ribonucleoside binding / ribonucleoside binding /  fibrillar center / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / fibrillar center / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity /  DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cell population proliferation / transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / cell population proliferation / transcription by RNA polymerase II /  nucleic acid binding / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / molecular adaptor activity / nucleic acid binding / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / molecular adaptor activity /  nuclear body / nuclear body /  protein dimerization activity / protein heterodimerization activity / protein dimerization activity / protein heterodimerization activity /  nucleotide binding / nucleotide binding /  mRNA binding / DNA-templated transcription / mRNA binding / DNA-templated transcription /  chromatin binding / chromatin binding /  chromatin / chromatin /  nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleolus / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II /  DNA binding / DNA binding /  RNA binding / zinc ion binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding /  nucleoplasm / nucleoplasm /  membrane / membrane /  metal ion binding metal ion bindingSimilarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Sus scrofa (pig) Sus scrofa (pig)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Vos, S.M. / Su, B.G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2024Title: Distinct negative elongation factor conformations regulate RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing. Authors: Bonnie G Su / Seychelle M Vos /  Abstract: Metazoan gene expression regulation involves pausing of RNA polymerase (Pol II) in the promoter-proximal region of genes and is stabilized by DSIF and NELF. Upon depletion of elongation factors, NELF ...Metazoan gene expression regulation involves pausing of RNA polymerase (Pol II) in the promoter-proximal region of genes and is stabilized by DSIF and NELF. Upon depletion of elongation factors, NELF appears to accompany elongating Pol II past pause sites; however, prior work indicates that NELF prevents Pol II elongation. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of Pol II-DSIF-NELF complexes with NELF in two distinct conformations corresponding to paused and poised states. The paused NELF state supports Pol II stalling, whereas the poised NELF state enables transcription elongation as it does not support a tilted RNA-DNA hybrid. Further, the poised NELF state can accommodate TFIIS binding to Pol II, allowing for Pol II reactivation at paused or backtracking sites. Finally, we observe that the NELF-A tentacle interacts with the RPB2 protrusion and is necessary for pausing. Our results define how NELF can support pausing, reactivation, and elongation by Pol II. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uhg.cif.gz 8uhg.cif.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uhg.ent.gz pdb8uhg.ent.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uhg.json.gz 8uhg.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uhg https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uhg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uhg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/uh/8uhg | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42280MC  8uhaC  8uhdC 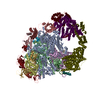 8ui0C  8uisC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Negative elongation factor ... , 4 types, 4 molecules XVWU
| #1: Protein | Mass: 43320.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFE, RD, RDBP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFE, RD, RDBP / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P18615 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P18615 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 63233.250 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFB, COBRA1, KIAA1182 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFB, COBRA1, KIAA1182 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8WX92 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8WX92 |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 66315.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFCD, NELFD, TH1, TH1L, HSPC130 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFCD, NELFD, TH1, TH1L, HSPC130 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8IXH7 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8IXH7 |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 57343.598 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFA, WHSC2, P/OKcl.15 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NELFA, WHSC2, P/OKcl.15 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H3P2 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H3P2 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase ... , 7 types, 7 molecules ABCEGIK
| #4: Protein |  Polymerase PolymeraseMass: 217450.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) Sus scrofa (pig)References: UniProt: A0A8D1DPV6,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein |  Polymerase PolymeraseMass: 134041.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) Sus scrofa (pig)References: UniProt: A0A4X1TVZ5,  DNA-directed RNA polymerase DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #6: Protein |  Polymerase PolymeraseMass: 30997.557 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A481DF93 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A481DF93 |
| #8: Protein |  Polymerase / RPB5 Polymerase / RPB5Mass: 24644.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VTX4 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VTX4 |
| #10: Protein |  Polymerase PolymeraseMass: 19227.205 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VKG7 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VKG7 |
| #12: Protein |  Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit I / RNA polymerase II 14.5 ...RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit I / RNA polymerase II 14.5 kDa subunit / RPB14.5 Polymerase / RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit I / RNA polymerase II 14.5 ...RNA polymerase II subunit B9 / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit I / RNA polymerase II 14.5 kDa subunit / RPB14.5Mass: 14541.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: P60899 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: P60899 |
| #14: Protein |  Polymerase PolymeraseMass: 13068.013 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: F1RKE4 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: F1RKE4 |
-RNA polymerase ... , 2 types, 2 molecules DL
| #7: Protein | Mass: 16331.255 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8D0KES4 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8D0KES4 |
|---|---|
| #15: Protein |  Mass: 7018.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1TRS6 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1TRS6 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 3 types, 3 molecules FHJ
| #9: Protein |  RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit F / RPB6 homolog RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit F / RPB6 homologMass: 14477.001 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VEK9 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A4X1VEK9 |
|---|---|
| #11: Protein |  RNA polymerase RNA polymeraseMass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8D1AQR7 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8D1AQR7 |
| #13: Protein |  RNA polymerase RNA polymeraseMass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8W4F9W9 Sus scrofa (pig) / References: UniProt: A0A8W4F9W9 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 15409.860 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #18: DNA chain | Mass: 11728.553 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-RNA chain / Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules PZ
| #17: RNA chain |  Mass: 5077.007 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #20: Protein | Mass: 121145.477 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SUPT5H, SPT5, SPT5H / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SUPT5H, SPT5, SPT5H / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: O00267 Escherichia coli (E. coli) / References: UniProt: O00267 |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 9 molecules 


| #21: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #22: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RNA Polymerase in complex with DSIF and NELF / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4, #6-#20 / Source: NATURAL / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4, #6-#20 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Sus scrofa (pig) Sus scrofa (pig) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES |
Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm Bright-field microscopy / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 90283 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj





































































