[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9pdd: 22bin20S complex (NSF-alphaSNAP-2:2 syntaxin-1a:SNAP-25), hydroly... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9pdd | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
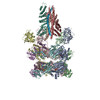
| Title | 22bin20S complex (NSF-alphaSNAP-2:2 syntaxin-1a:SNAP-25), hydrolyzing, class 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / ATPase / SNARE / hydrolysis / disassembly / translocation / exocytosis / neurotransmitter release / synapse / synaptic transmission / membrane fusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIntra-Golgi traffic / Retrograde transport at the Trans-Golgi-Network / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / soluble NSF attachment protein activity / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / SNARE complex disassembly / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming ...Intra-Golgi traffic / Retrograde transport at the Trans-Golgi-Network / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / soluble NSF attachment protein activity / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / SNARE complex disassembly / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming / protein-containing complex disassembly / ATP-dependent protein disaggregase activity / positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity / intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / Golgi stack / apical protein localization / syntaxin binding / vesicle-fusing ATPase / syntaxin-1 binding / synaptic vesicle priming / positive regulation of receptor recycling / presynaptic active zone membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / SNARE binding / PDZ domain binding / neuromuscular junction / intracellular protein transport / potassium ion transport / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / brain development / neuron differentiation / terminal bouton / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / presynapse / midbody / membrane fusion / postsynapse / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.16 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | White, K.I. / Brunger, A.T. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural remodeling of target-SNARE protein complexes by NSF enables synaptic transmission. Authors: K Ian White / Yousuf A Khan / Kangqiang Qiu / Ashwin Balaji / Sergio Couoh-Cardel / Luis Esquivies / Richard A Pfuetzner / Jiajie Diao / Axel T Brunger /  Abstract: Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with the plasma membrane upon the arrival of an action potential at the active zone. Multiple proteins organize trans-SNARE complex assembly and ...Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with the plasma membrane upon the arrival of an action potential at the active zone. Multiple proteins organize trans-SNARE complex assembly and priming, leading to fusion. One target membrane SNARE, syntaxin, forms nanodomains at the active zone, and another, SNAP-25, enters non-fusogenic complexes with it. Here, we reveal mechanistic details of AAA+ protein NSF (N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor) and SNAP (soluble NSF attachment protein) action before fusion. We show that syntaxin clusters are conserved, that NSF colocalizes with them, and characterize SNARE populations that may exist within or near them using cryo-EM. Supercomplexes of NSF, α-SNAP, and either a syntaxin tetramer or one of two binary complexes of syntaxin-SNAP-25 reveal atomic details of SNARE processing and show how sequential ATP hydrolysis drives disassembly. These results suggest a functional role for syntaxin clusters as reservoirs and a corresponding role for NSF in syntaxin liberation and SNARE protein quality control preceding fusion. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Title: Structural remodeling of target-SNARE protein complexes by NSF enables synaptic transmission. Authors: K Ian White / Yousuf A Khan / Kangqiang Qiu / Ashwin Balaji / Sergio Couoh-Cardel / Luis Esquivies / Richard A Pfuetzner / Jiajie Diao / Axel T Brunger /  Abstract: Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with the plasma membrane upon the arrival of an action potential at the active zone. Multiple proteins organize trans-SNARE complex assembly and ...Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with the plasma membrane upon the arrival of an action potential at the active zone. Multiple proteins organize trans-SNARE complex assembly and priming, leading to fusion. One target membrane SNARE, syntaxin, forms nanodomains at the active zone, and another, SNAP-25, enters non-fusogenic complexes with it. Here, we reveal mechanistic details of AAA+ protein NSF (N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor) and SNAP (soluble NSF attachment protein) action before fusion. We show that syntaxin clusters are conserved, that NSF colocalizes with them, and characterize SNARE populations that may exist within or near them using cryo-EM. Supercomplexes of NSF, α-SNAP, and either a syntaxin tetramer or one of two binary complexes of syntaxin-SNAP-25 reveal atomic details of SNARE processing and show how sequential ATP hydrolysis drives disassembly. These results suggest a functional role for syntaxin clusters as reservoirs and a corresponding role for NSF in syntaxin liberation and SNARE protein quality control preceding fusion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9pdd.cif.gz 9pdd.cif.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9pdd.ent.gz pdb9pdd.ent.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9pdd.json.gz 9pdd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pd/9pdd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pd/9pdd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pd/9pdd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pd/9pdd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  71533MC  9ojrC  9ojuC  9ojzC  9ok3C  9ok5C  9okcC  9oljC  9oloC  9om6C  9omqC  9pafC  9pagC  9pb9C  9pbaC  9pbfC  9pbvC  9pc3C  9pcxC  9pczC  9pd1C  9pd8C  9pdbC  9pf2C  9pfcC  9pffC  9pfgC  9oj2  9ojj C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 10 molecules ABCDEFIJKL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 82907.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | Mass: 33290.715 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1124.378 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 15 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 33.96 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1889717 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.16 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 35805 / Algorithm: EXACT BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6MDM Accession code: 6MDM / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




























 PDBj
PDBj