[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
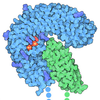
Yorodumi- PDB-9jta: Crystal structure of RNF213 RING domain bound to IpaH1.4 LRR domain -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9jta | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of RNF213 RING domain bound to IpaH1.4 LRR domain | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / RNF213 / IpaH1.4 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmodulation of process of another organism / lipid ubiquitination / negative regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway / lipid droplet formation / xenophagy / Suppression of apoptosis / sprouting angiogenesis / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Aminoacyltransferases / regulation of lipid metabolic process / protein K63-linked ubiquitination ...modulation of process of another organism / lipid ubiquitination / negative regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway / lipid droplet formation / xenophagy / Suppression of apoptosis / sprouting angiogenesis / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Aminoacyltransferases / regulation of lipid metabolic process / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / immune system process / protein autoubiquitination / lipid droplet / RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Signaling by ALK fusions and activated point mutants / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / angiogenesis / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / host cell cytoplasm / defense response to bacterium / protein ubiquitination / nucleolus / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Shigella flexneri 5a str. M90T (bacteria) Shigella flexneri 5a str. M90T (bacteria) Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.7 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou, X.D. / Wang, Y.R. / Pan, L.F. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Shigella effector IpaH1.4 subverts host E3 ligase RNF213 to evade antibacterial immunity. Authors: Xindi Zhou / Huijing Zhang / Yaru Wang / Danni Wang / Zhiqiao Lin / Yuchao Zhang / Yubin Tang / Jianping Liu / Yu-Feng Yao / Yixiao Zhang / Lifeng Pan /  Abstract: Ubiquitination plays vital roles in modulating pathogen-host cell interactions. RNF213, a E3 ligase, can catalyze the ubiquitination of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and is crucial for antibacterial ...Ubiquitination plays vital roles in modulating pathogen-host cell interactions. RNF213, a E3 ligase, can catalyze the ubiquitination of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and is crucial for antibacterial immunity in mammals. Shigella flexneri, an LPS-containing pathogenic bacterium, has developed mechanisms to evade host antibacterial defenses during infection. However, the precise strategies by which S. flexneri circumvents RNF213-mediated antibacterial immunity remain poorly understood. Here, through comprehensive biochemical, structural and cellular analyses, we reveal that the E3 effector IpaH1.4 of S. flexneri can directly target human RNF213 via a specific interaction between the IpaH1.4 LRR domain and the RING domain of RNF213, and mediate the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of RNF213 in cells. Furthermore, we determine the cryo-EM structure of human RNF213 and the crystal structure of the IpaH1.4 LRR/RNF213 RING complex, elucidating the molecular mechanism underlying the specific recognition of RNF213 by IpaH1.4. Finally, our cell based functional assays demonstrate that the targeting of host RNF213 by IpaH1.4 promotes S. flexneri proliferation within infected cells. In summary, our work uncovers an unprecedented strategy employed by S. flexneri to subvert the key host immune factor RNF213, thereby facilitating bacterial proliferation during invasion. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9jta.cif.gz 9jta.cif.gz | 142.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9jta.ent.gz pdb9jta.ent.gz | 104.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9jta.json.gz 9jta.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jt/9jta https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jt/9jta ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jt/9jta ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jt/9jta | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9jw1C  9jwgC  7v8eS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 26636.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Shigella flexneri 5a str. M90T (bacteria) Shigella flexneri 5a str. M90T (bacteria)Gene: EKN05_024115 / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A4P7TTK5, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 7458.644 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF213, ALO17, C17orf27, KIAA1554, KIAA1618, MYSTR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RNF213, ALO17, C17orf27, KIAA1554, KIAA1618, MYSTR / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q63HN8, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement, Transferases; ...References: UniProt: Q63HN8, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement, Transferases; Acyltransferases; Aminoacyltransferases | ||||||
| #3: Chemical | | #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.55 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 51.74 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 289 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7.8 Details: 0.1 M HEPES (pH 7.8), 0.2 M Ammonium acetate, 20% (w/v) polyethylene glycol 3,350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRF SSRF  / Beamline: BL02U1 / Wavelength: 0.97918 Å / Beamline: BL02U1 / Wavelength: 0.97918 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER2 S 9M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jan 13, 2024 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.97918 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.7→62.22 Å / Num. obs: 39533 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 25.5 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 32.8 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.063 / Net I/σ(I): 26.6 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.702→1.731 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.531 / Num. unique obs: 1927 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 7V8E Resolution: 1.7→29.38 Å / SU ML: 0.2484 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 22.5554 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.1 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 45.93 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.7→29.38 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj