[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9jb1: Cryo-EM structure of the type I amyloid-beta 42 fibril containing... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9jb1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
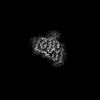
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the type I amyloid-beta 42 fibril containing a D-Asp at positions 7 and 23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Amyloid-beta precursor protein | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / aggregation | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationamyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process ...amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / axon midline choice point recognition / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / regulation of synapse structure or activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / growth factor receptor binding / peptidase activator activity / Golgi-associated vesicle / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / astrocyte projection / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / dendrite development / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / signaling receptor activator activity / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / transition metal ion binding / main axon / The NLRP3 inflammasome / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of multicellular organism growth / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of T cell migration / response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus / neuronal dense core vesicle / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / positive regulation of chemokine production / cellular response to manganese ion / Notch signaling pathway / swimming behavior / extracellular matrix organization / neuron projection maintenance / clathrin-coated pit / astrocyte activation / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / axonogenesis / Mitochondrial protein degradation / platelet alpha granule lumen / response to interleukin-1 / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to cAMP / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / positive regulation of glycolytic process / dendritic shaft / endosome lumen / trans-Golgi network membrane / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / central nervous system development / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / learning / adult locomotory behavior / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / locomotory behavior / microglial cell activation / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / synapse organization / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / visual learning / recycling endosome / positive regulation of JNK cascade / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / response to lead ion / Golgi lumen / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / endocytosis / cellular response to amyloid-beta / neuron projection development / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / calcium ion transport / Platelet degranulation / regulation of translation / heparin binding / regulation of gene expression Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hsiao, L.C. / Lee, C.H. / Hsu, M.F. / Hsu, S.T. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Taiwan, 1items Taiwan, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Impacts of D-aspartate on the Aggregation Kinetics and Structural Polymorphism of Amyloid β Peptide 1-42. Authors: Li-Ching Hsiao / Chih-Hsuan Lee / Karine Mazmanian / Masaya Yoshida / Genta Ito / Takuya Murata / Naoko Utsunomiya-Tate / Takeharu Haino / Shih-Ichi Tate / Shang-Te Danny Hsu /   Abstract: Isomerization of L-Aspartate (L-Asp) into D-aspartate (D-Asp) occurs naturally in proteins at a rate that is much faster than that of other amino acid types. Accumulation of D-Asp is age-dependent, ...Isomerization of L-Aspartate (L-Asp) into D-aspartate (D-Asp) occurs naturally in proteins at a rate that is much faster than that of other amino acid types. Accumulation of D-Asp is age-dependent, which could alter protein structures and, therefore, functions. Site-specific introduction of D-Asp can accelerate aggregation kinetics of a variety of proteins associated with misfolding diseases. Here, we showed by thioflavin T fluorescence that the isomerization of L-Asp at different positions of amyloid β peptide 1-42 (Aβ42) generates opposing effects on its aggregation kinetics. We further determined the atomic structures of Aβ42 amyloid fibrils harboring a single D-Asp at position 23 and two D-Asp at positions 7 and 23 by cryo-electron microscopy helical reconstruction - cross-validated by cryo-electron tomography and atomic force microscopy - to reveal how D-Asp contributes to the formation of a unique triple stranded amyloid fibril structure stabilized by two threads of well-ordered water molecules. These findings provide crucial insights into how the conversion from L- to D-Asp influences the aggregation propensity and amyloid polymorphism of Aβ42. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9jb1.cif.gz 9jb1.cif.gz | 77.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9jb1.ent.gz pdb9jb1.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9jb1.json.gz 9jb1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jb/9jb1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jb/9jb1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jb/9jb1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jb/9jb1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  61304MC  9jazC  9jb0C  9jb2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4520.087 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P05067 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P05067Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Type I amyloid-beta 42 fibril containing a D-Asp at positions 7 and 23 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: brain Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: brain |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1400 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21.1_5286: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 178.86 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 2.38 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 89380 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj