+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 9isb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
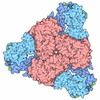
| タイトル | Ligand bound AGD of enzyme | ||||||
 要素 要素 | Protein acetyltransferase | ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | TRANSFERASE / Acetyltransferase | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報acyltransferase activity, transferring groups other than amino-acyl groups / ATP binding / metal ion binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  | ||||||
| 手法 |  X線回折 / X線回折 /  シンクロトロン / シンクロトロン /  分子置換 / 解像度: 2.24 Å 分子置換 / 解像度: 2.24 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Park, J.B. / Roh, S.H. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  韓国, 1件 韓国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2025 ジャーナル: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / 年: 2025タイトル: Structural basis of the catalytic and allosteric mechanism of bacterial acetyltransferase PatZ. 著者: Jun Bae Park / Gwanwoo Lee / Yu-Yeon Han / Dongwook Kim / Kyoo Heo / Jeesoo Kim / Juhee Park / Hyosuk Yun / Chul Won Lee / Hyun-Soo Cho / Jong-Seo Kim / Martin Steinegger / Yeong-Jae Seok / Soung-Hun Roh /  要旨: GCN5-related -acetyltransferases (GNATs) are essential for regulating bacterial metabolism by acetylating specific target proteins. Despite their importance in bacterial physiology, the mechanisms ...GCN5-related -acetyltransferases (GNATs) are essential for regulating bacterial metabolism by acetylating specific target proteins. Despite their importance in bacterial physiology, the mechanisms behind their enzymatic and regulatory functions remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the structures of protein acetyltransferase Z (PatZ), a Type I GNAT, and examined its ligand interactions, catalytic mechanism, and allosteric regulation. PatZ functions as a homotetramer, with each subunit comprising a catalytic and a regulatory domain. Our results demonstrate that the regulatory domain is vital for acetyltransferase activity, as it triggers cooperative conformational changes in the catalytic domain and directly aids in the formation of substrate-binding pockets. Additionally, a protein structure-based evolutionary analysis of bacterial GNAT types revealed a distinct regulatory domain pattern across phyla, highlighting its crucial role in responding to cellular energy levels. #1: ジャーナル: mBio / 年: 2018 タイトル: Identification of Novel Protein Lysine Acetyltransferases in Escherichia coli. 著者: David G Christensen / Jesse G Meyer / Jackson T Baumgartner / Alexandria K D'Souza / William C Nelson / Samuel H Payne / Misty L Kuhn / Birgit Schilling / Alan J Wolfe /  要旨: Posttranslational modifications, such as ε-lysine acetylation, regulate protein function. ε-lysine acetylation can occur either nonenzymatically or enzymatically. The nonenzymatic mechanism uses ...Posttranslational modifications, such as ε-lysine acetylation, regulate protein function. ε-lysine acetylation can occur either nonenzymatically or enzymatically. The nonenzymatic mechanism uses acetyl phosphate (AcP) or acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) as acetyl donor to modify an ε-lysine residue of a protein. The enzymatic mechanism uses ε-lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) to specifically transfer an acetyl group from AcCoA to ε-lysine residues on proteins. To date, only one KAT (YfiQ, also known as Pka and PatZ) has been identified in Here, we demonstrate the existence of 4 additional KATs: RimI, YiaC, YjaB, and PhnO. In a genetic background devoid of all known acetylation mechanisms (most notably AcP and YfiQ) and one deacetylase (CobB), overexpression of these putative KATs elicited unique patterns of protein acetylation. We mutated key active site residues and found that most of them eliminated enzymatic acetylation activity. We used mass spectrometry to identify and quantify the specificity of YfiQ and the four novel KATs. Surprisingly, our analysis revealed a high degree of substrate specificity. The overlap between KAT-dependent and AcP-dependent acetylation was extremely limited, supporting the hypothesis that these two acetylation mechanisms play distinct roles in the posttranslational modification of bacterial proteins. We further showed that these novel KATs are conserved across broad swaths of bacterial phylogeny. Finally, we determined that one of the novel KATs (YiaC) and the known KAT (YfiQ) can negatively regulate bacterial migration. Together, these results emphasize distinct and specific nonenzymatic and enzymatic protein acetylation mechanisms present in bacteria.ε-Lysine acetylation is one of the most abundant and important posttranslational modifications across all domains of life. One of the best-studied effects of acetylation occurs in eukaryotes, where acetylation of histone tails activates gene transcription. Although bacteria do not have true histones, ε-lysine acetylation is prevalent; however, the role of these modifications is mostly unknown. We constructed an strain that lacked both known acetylation mechanisms to identify four new ε-lysine acetyltransferases (RimI, YiaC, YjaB, and PhnO). We used mass spectrometry to determine the substrate specificity of these acetyltransferases. Structural analysis of selected substrate proteins revealed site-specific preferences for enzymatic acetylation that had little overlap with the preferences of the previously reported acetyl-phosphate nonenzymatic acetylation mechanism. Finally, YiaC and YfiQ appear to regulate flagellum-based motility, a phenotype critical for pathogenesis of many organisms. These acetyltransferases are highly conserved and reveal deeper and more complex roles for bacterial posttranslational modification. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  9isb.cif.gz 9isb.cif.gz | 106.7 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb9isb.ent.gz pdb9isb.ent.gz | 78.7 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  9isb.json.gz 9isb.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  9isb_validation.pdf.gz 9isb_validation.pdf.gz | 1020.6 KB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  9isb_full_validation.pdf.gz 9isb_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  9isb_validation.xml.gz 9isb_validation.xml.gz | 22.7 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  9isb_validation.cif.gz 9isb_validation.cif.gz | 29.8 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/is/9isb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/is/9isb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/is/9isb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/is/9isb | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  9isqC  9it0C C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 単位格子 |
|
- 要素
要素
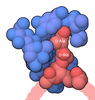
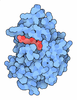
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 25477.389 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 由来: (組換発現)  遺伝子: pat, yfiQ, ACU57_10170, BGM66_000644, BJI68_02105, C0P57_000002, CG831_000342, CIG67_15390, CTR35_002231, CV83915_03530, DTL43_02095, EIZ93_15170, FOI11_000020, FOI11_20030, FWK02_03775, ...遺伝子: pat, yfiQ, ACU57_10170, BGM66_000644, BJI68_02105, C0P57_000002, CG831_000342, CIG67_15390, CTR35_002231, CV83915_03530, DTL43_02095, EIZ93_15170, FOI11_000020, FOI11_20030, FWK02_03775, G3V95_05750, G4A38_06870, G4A47_19960, GNW61_15560, GOP25_16215, GQM21_00025, GRW05_03440, HMV95_11440, J0541_000369, JNP96_20710, QDW62_06300, SAMEA3752557_00912 発現宿主:  #2: 化合物 | ChemComp-ADP / | #3: 化合物 | ChemComp-ATP / | #4: 水 | ChemComp-HOH / | 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法:  X線回折 / 使用した結晶の数: 1 X線回折 / 使用した結晶の数: 1 |
|---|
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 結晶 | マシュー密度: 2.89 Å3/Da / 溶媒含有率: 57.45 % |
|---|---|
| 結晶化 | 温度: 290 K / 手法: 蒸気拡散法, ハンギングドロップ法 詳細: 0.2 M potassium sodium tartrate, 20% (w/v) PEG 3350. |
-データ収集
| 回折 | 平均測定温度: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| 放射光源 | 由来:  シンクロトロン / サイト: PAL/PLS シンクロトロン / サイト: PAL/PLS  / ビームライン: 5C (4A) / 波長: 0.97942 Å / ビームライン: 5C (4A) / 波長: 0.97942 Å |
| 検出器 | タイプ: DECTRIS EIGER X 9M / 検出器: PIXEL / 日付: 2022年5月29日 |
| 放射 | プロトコル: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / 単色(M)・ラウエ(L): M / 散乱光タイプ: x-ray |
| 放射波長 | 波長: 0.97942 Å / 相対比: 1 |
| 反射 | 解像度: 2.24→99.57 Å / Num. obs: 28802 / % possible obs: 99.8 % / 冗長度: 20 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 36.26 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.101 / Net I/σ(I): 20.2 |
| 反射 シェル | 解像度: 2.24→2.32 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.834 / Num. unique obs: 2880 |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 精密化 | 構造決定の手法:  分子置換 分子置換開始モデル: AGD 解像度: 2.24→71.05 Å / SU ML: 0.2601 / 交差検証法: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / 位相誤差: 28.5918 立体化学のターゲット値: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 溶媒の処理 | 減衰半径: 0.9 Å / VDWプローブ半径: 1.1 Å / 溶媒モデル: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子変位パラメータ | Biso mean: 49.89 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 精密化ステップ | サイクル: LAST / 解像度: 2.24→71.05 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS精密化 シェル |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー













 PDBj
PDBj