+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9gvq | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
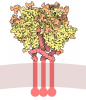
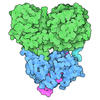
| Title | MUC5AC mucin amino acids 28 to 1483 | |||||||||
 Components Components | Mucin-5AC | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / mucin / lung / filament / polymer / disulfide | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmucus layer / Defective GALNT3 causes HFTC / Defective C1GALT1C1 causes TNPS / Defective GALNT12 causes CRCS1 / Termination of O-glycan biosynthesis / O-linked glycosylation of mucins / extracellular matrix structural constituent / Dectin-2 family / extracellular matrix / Golgi lumen ...mucus layer / Defective GALNT3 causes HFTC / Defective C1GALT1C1 causes TNPS / Defective GALNT12 causes CRCS1 / Termination of O-glycan biosynthesis / O-linked glycosylation of mucins / extracellular matrix structural constituent / Dectin-2 family / extracellular matrix / Golgi lumen / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Haberman, M. / Kamyshinsky, R. / Fass, D. | |||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Israel, 2items Israel, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: MUC5AC filaments illuminate the structural diversification of respiratory and intestinal mucins. Authors: Meital Haberman / Roman Kamyshinsky / Nava Reznik / Noa Yeshaya / Lev Khmelnitsky / Elizabeth G Plender / Evan E Eichler / Deborah Fass /   Abstract: Secreted mucins are multimegadalton glycoprotein polymers that share the function of protecting mucosal tissues but diversified for activities in different organs of the body. Structural studies of ...Secreted mucins are multimegadalton glycoprotein polymers that share the function of protecting mucosal tissues but diversified for activities in different organs of the body. Structural studies of secreted mucins are complicated by the enormous sizes, flexibility, and complex supramolecular assembly modes of these glycoproteins. The two major respiratory mucins are MUC5AC and MUC5B. Here, we present structures of a large amino-terminal segment of MUC5AC in the form of helical filaments. These filaments differ from filamentous and tubular structures observed previously for the intestinal mucin MUC2 and the partial mucin homolog VWF. Nevertheless, the MUC5AC helical filaments support the proposed mechanism, based on MUC2 and VWF, for how noncovalent interactions between mucin monomers guide disulfide crosslinking to form polymers. The high-resolution MUC5AC structures show how local and limited changes in amino acid sequence can profoundly affect higher-order assembly while preserving the overall folds and polymerization activity of mucin glycoproteins. Differences in supramolecular assembly are likely to be functionally significant considering the divergence of mechanical properties and physiological requirements between respiratory and intestinal mucins. Determining the high-resolution structures of respiratory mucins provides a foundation for understanding the mechanisms by which they clean and protect the lungs. Moreover, the MUC5AC structure enables visualization of the sites of human amino acid sequence variation and disease-associated mutations. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9gvq.cif.gz 9gvq.cif.gz | 894.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9gvq.ent.gz pdb9gvq.ent.gz | 708.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9gvq.json.gz 9gvq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gv/9gvq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gv/9gvq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gv/9gvq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gv/9gvq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  51639MC  9gvjC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 157080.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MUC5AC, MUC5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MUC5AC, MUC5 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P98088 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P98088#2: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CU / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: filament of the MUC5AC amino-terminal segment / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: secreted / Tissue: lung Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: secreted / Tissue: lung | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293F / Plasmid: pCDNA3.1 Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293F / Plasmid: pCDNA3.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 5.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.45 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 45 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 74 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 94 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 165735 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj