[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9fch: P116 dimer in the full state (PDB structure of the full-length ec... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9fch | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | P116 dimer in the full state (PDB structure of the full-length ectodomain truncated to amino acids 246-818) | ||||||
 Components Components | Uncharacterized protein MG075 homolog | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID BINDING PROTEIN / Lipid Transfer Protein / Mycoplasma pneumoniae | ||||||
| Function / homology | : / : / P116-like protein / membrane / Uncharacterized protein MG075 homolog Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria) Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.52 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Mager, S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025Title: How does scavenge lipids from its host membranes? Authors: Sina Manger / Serena M Arghittu / Lasse Sprankel / Jakob Meier-Credo / Konstantin Wieland / Daniela Bublak / Julian Langer / Roberto Covino / Achilleas S Frangakis /  Abstract: Lipid acquisition and transport are fundamental processes in all organisms. Here, we investigate the lipid uptake and delivery mechanism of the minimal model organism . We show that the essential ...Lipid acquisition and transport are fundamental processes in all organisms. Here, we investigate the lipid uptake and delivery mechanism of the minimal model organism . We show that the essential protein P116 can transport lipids between liposomes independently and without adenosine 5'-triphosphate consumption. Our structural data and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the mechanism by which the amino-terminal region of P116 perturbs the membrane, the lipid transfer route, and the regulation of membrane binding by the cargo mass within P116's large hydrophobic cavity. When adequately filled with cargo, P116 undergoes a rapid conformational change that modulates membrane binding. Together, our results show that developed an integrated lipid uptake and delivery machinery that simplifies the complex multiprotein pathways used by higher developed organisms. #1:  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Essential protein P116 extracts cholesterol and other indispensable lipids for Mycoplasmas. Authors: Lasse Sprankel / David Vizarraga / Jesús Martín / Sina Manger / Jakob Meier-Credo / Marina Marcos / Josep Julve / Noemi Rotllan / Margot P Scheffer / Joan Carles Escolà-Gil / Julian D ...Authors: Lasse Sprankel / David Vizarraga / Jesús Martín / Sina Manger / Jakob Meier-Credo / Marina Marcos / Josep Julve / Noemi Rotllan / Margot P Scheffer / Joan Carles Escolà-Gil / Julian D Langer / Jaume Piñol / Ignacio Fita / Achilleas S Frangakis /   Abstract: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, responsible for approximately 30% of community-acquired human pneumonia, needs to extract lipids from the host environment for survival and proliferation. Here, we report a ...Mycoplasma pneumoniae, responsible for approximately 30% of community-acquired human pneumonia, needs to extract lipids from the host environment for survival and proliferation. Here, we report a comprehensive structural and functional analysis of the previously uncharacterized protein P116 (MPN_213). Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of P116 reveals a homodimer presenting a previously unseen fold, forming a huge hydrophobic cavity, which is fully accessible to solvent. Lipidomics analysis shows that P116 specifically extracts lipids such as phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin and cholesterol. Structures of different conformational states reveal the mechanism by which lipids are extracted. This finding immediately suggests a way to control Mycoplasma infection by interfering with lipid uptake. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9fch.cif.gz 9fch.cif.gz | 226.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9fch.ent.gz pdb9fch.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9fch.json.gz 9fch.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fc/9fch https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fc/9fch ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fc/9fch ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fc/9fch | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  50314MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 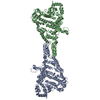
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 64386.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria) Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria)Gene: MPN_213, G07_orf1030, MP618 / Production host:  Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: P116 from Mycoplasma pneumoniae (aa 246-818; full state) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria) Mycoplasmoides pneumoniae M129 (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: 20 mM Tris-HCl |
| Specimen | Conc.: 3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 4 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.52 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 145945 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj