[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9ed1: Cryo-EM structure of the human KCa3.1/calmodulin channel in compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9ed1 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
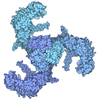
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human KCa3.1/calmodulin channel in complex with Ca2+ and 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP-103) | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Ion channel / Membrane protein / Ca-binding protein | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / saliva secretion / small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / stabilization of membrane potential / Ca2+ activated K+ channels / macropinocytosis / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / : / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / saliva secretion / small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / stabilization of membrane potential / Ca2+ activated K+ channels / macropinocytosis / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / : / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / establishment of protein localization to membrane / cell volume homeostasis / phospholipid translocation / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / nitric-oxide synthase binding / presynaptic endocytosis / calcineurin-mediated signaling / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / adenylate cyclase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / immune system process / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / potassium channel activity / postsynaptic cytosol / catalytic complex / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / calcium channel inhibitor activity / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / regulation of heart rate / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / response to amphetamine / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of protein secretion / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / establishment of localization in cell / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / calcium channel regulator activity / potassium ion transport / defense response / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / ruffle membrane / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding / calcium ion transport / myelin sheath / sperm midpiece / growth cone / protein phosphatase binding / vesicle / protein homotetramerization / transmembrane transporter binding / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / protein domain specific binding / neuronal cell body / calcium ion binding / centrosome / protein kinase binding / protein homodimerization activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nam, Y.W. / Zhang, M. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: Design and structural basis of selective 1,4-dihydropyridine inhibitors of the calcium-activated potassium channel K3.1. Authors: Seow Theng Ong / Young-Woo Nam / Joshua A Nasburg / Alena Ramanishka / Xuan Rui Ng / Zhong Zhuang / Stephanie Shee Min Goay / Hai M Nguyen / Latika Singh / Vikrant Singh / Alicia Rivera / M ...Authors: Seow Theng Ong / Young-Woo Nam / Joshua A Nasburg / Alena Ramanishka / Xuan Rui Ng / Zhong Zhuang / Stephanie Shee Min Goay / Hai M Nguyen / Latika Singh / Vikrant Singh / Alicia Rivera / M Elaine Eyster / Yang Xu / Seth L Alper / Heike Wulff / Miao Zhang / K George Chandy /   Abstract: The 1,4-dihydropyridines, drugs with well-established bioavailability and toxicity profiles, have proven efficacy in treating human hypertension, peripheral vascular disorders, and coronary artery ...The 1,4-dihydropyridines, drugs with well-established bioavailability and toxicity profiles, have proven efficacy in treating human hypertension, peripheral vascular disorders, and coronary artery disease. Every 1,4-dihydropyridine in clinical use blocks L-type voltage-gated calcium channels. We now report our development, using selective optimization of a side activity (SOSA), of a class of 1,4-dihydropyridines that selectively and potently inhibit the intermediate-conductance calcium-activated K channel K3.1, a validated therapeutic target for diseases affecting many organ systems. One of these 1,4-dihydropyridines, DHP-103, blocked K3.1 with an IC of 6 nM and exhibited exquisite selectivity over calcium channels and a panel of >100 additional molecular targets. Using high-resolution structure determination by cryogenic electron microscopy together with mutagenesis and electrophysiology, we delineated the drug binding pocket for DHP-103 within the water-filled central cavity of the K3.1 channel pore, where bound drug directly impedes ion permeation. DHP-103 inhibited gain-of-function mutant K3.1 channels that cause hereditary xerocytosis, suggesting its potential use as a therapeutic for this hemolytic anemia. In a rat model of acute ischemic stroke, the second leading cause of death worldwide, DHP-103 administered 12 h postischemic insult in proof-of-concept studies reduced infarct volume, improved balance beam performance (measure of proprioception) and decreased numbers of activated microglia in infarcted areas. K3.1-selective 1,4-dihydropyridines hold promise for the many diseases for which K3.1 has been experimentally confirmed as a therapeutic target. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9ed1.cif.gz 9ed1.cif.gz | 343.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9ed1.ent.gz pdb9ed1.ent.gz | 280 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9ed1.json.gz 9ed1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/9ed1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/9ed1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/9ed1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/9ed1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  47930MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42598.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNN4, IK1, IKCA1, KCA4, SK4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNN4, IK1, IKCA1, KCA4, SK4 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15554 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15554#2: Protein | Mass: 16406.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP29 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP29#3: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human SK4-CaM channel complex in the presence of calcium. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.23166 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293s / Cell: HEK293s / Plasmid: pEGBacMam Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: HEK293s / Cell: HEK293s / Plasmid: pEGBacMam |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2300 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 109449 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj