[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
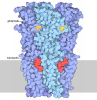
Yorodumi- PDB-9e4y: GluA2-gamma2 complex bound to memantine, glutamate, and cyclothiazide -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9e4y | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GluA2-gamma2 complex bound to memantine, glutamate, and cyclothiazide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / ligand-gated ion channel / ionotropic glutamate receptor / ampa receptor / ion channel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPresynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization / nervous system process ...Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / LGI-ADAM interactions / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / eye blink reflex / positive regulation of protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane / cerebellar mossy fiber / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / membrane hyperpolarization / nervous system process / protein targeting to membrane / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine head / cellular response to amine stimulus / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / neuromuscular junction development / perisynaptic space / Activation of AMPA receptors / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / transmission of nerve impulse / response to lithium ion / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / cellular response to glycine / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / conditioned place preference / regulation of receptor recycling / membrane depolarization / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / response to fungicide / cytoskeletal protein binding / glutamate-gated receptor activity / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / dendrite membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / synaptic membrane / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / regulation of membrane potential / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / PDZ domain binding / protein tetramerization / establishment of protein localization / postsynaptic density membrane / response to calcium ion / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / synaptic vesicle membrane / presynapse / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / presynaptic membrane / growth cone / scaffold protein binding / perikaryon / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / postsynaptic membrane / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / axon / external side of plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / synapse / dendrite / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Montano Romero, A. / Carrillo, E. / Jayaraman, V. / Twomey, E.C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Memantine inhibits calcium-permeable AMPA receptors. Authors: Elisa Carrillo / Alejandra Montaño Romero / Cuauhtemoc U Gonzalez / Andreea L Turcu / Santiago Vázquez / Edward C Twomey / Vasanthi Jayaraman /   Abstract: Memantine is an US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drug that is thought to selectively inhibit NMDA-subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDARs). NMDARs enable calcium influx into ...Memantine is an US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved drug that is thought to selectively inhibit NMDA-subtype of ionotropic glutamate receptors (NMDARs). NMDARs enable calcium influx into neurons and are critical for normal brain function. However, increasing evidence shows that calcium influx in neurological diseases is augmented by calcium-permeable AMPA-subtype ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPARs). Here, we demonstrate that these calcium-permeable AMPARs (CP-AMPARs) are inhibited by memantine. Electrophysiology unveils that memantine inhibition of CP-AMPARs is dependent on their calcium permeability and the presence of their neuronal auxiliary subunit transmembrane AMPAR regulatory proteins (TARPs). Through cryo-electron microscopy we elucidate that memantine blocks CP-AMPAR ion channels in a unique mechanism of action from NMDARs. Furthermore, we demonstrate that memantine inhibits a gain of function AMPAR mutation found in a patient with a neurodevelopmental disorder. Our findings unlock potential exploitation of this site to design more specific drugs targeting CP-AMPARs. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9e4y.cif.gz 9e4y.cif.gz | 691.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9e4y.ent.gz pdb9e4y.ent.gz | 563.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9e4y.json.gz 9e4y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/e4/9e4y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/e4/9e4y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/e4/9e4y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/e4/9e4y | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  47520MC  9e4zC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 90967.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19491 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19491#2: Protein | Mass: 23008.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O88602 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O88602#3: Chemical | ChemComp-377 / | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-GLU / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-CYZ / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GluA2-TARPgamma2 Complex bound to memantine, glutamate, and cyclothiazide Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #2 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293 Gnti- Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293 Gnti- |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 36557 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 4.3 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj