[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9dyf: Asenapine-bound serotonin 1A (5-HT1A) receptor-Gi1 protein complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9dyf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Asenapine-bound serotonin 1A (5-HT1A) receptor-Gi1 protein complex | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / GPCR Signaling Complex / Serotonin Receptor | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of serotonin secretion / Gi/o-coupled serotonin receptor activity / regulation of hormone secretion / regulation of behavior / receptor-receptor interaction / Serotonin receptors / serotonin receptor activity / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity / regulation of dopamine metabolic process / serotonin receptor signaling pathway ...regulation of serotonin secretion / Gi/o-coupled serotonin receptor activity / regulation of hormone secretion / regulation of behavior / receptor-receptor interaction / Serotonin receptors / serotonin receptor activity / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity / regulation of dopamine metabolic process / serotonin receptor signaling pathway / neurotransmitter receptor activity / serotonin metabolic process / serotonin binding / gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway / exploration behavior / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger / regulation of vasoconstriction / behavioral fear response / adenylate cyclase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / T cell migration / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway / D2 dopamine receptor binding / response to prostaglandin E / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to forskolin / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / negative regulation of insulin secretion / electron transport chain / G protein-coupled receptor binding / response to peptide hormone / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / centriolar satellite / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / GDP binding / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / G-protein beta-subunit binding / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / sensory perception of taste / extracellular vesicle / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / retina development in camera-type eye / G protein activity / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / midbody / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / cell cortex / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / chemical synaptic transmission / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Ras protein signal transduction / periplasmic space / electron transfer activity / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / ciliary basal body / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / iron ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.74 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Warren, A.L. / Zilberg, G. / Wacker, D. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025Title: Structural determinants of G protein subtype selectivity at the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A. Authors: Audrey L Warren / Gregory Zilberg / Anwar Abbassi / Alejandro Abraham / Shifan Yang / Daniel Wacker /  Abstract: Activation of the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A has been shown to regulate mood and cognition, making 5-HT1A an important target in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Although the ...Activation of the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A has been shown to regulate mood and cognition, making 5-HT1A an important target in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Although the receptor signals through inhibitory G proteins, more work is necessary to understand differences in transducer coupling and its relation to functional activity. To develop a molecular understanding of the differences underlying transducer coupling and activation, we performed structure-activity relationship studies of 5-HT1A with distinct G proteins. Through a combination of in vitro assays, we identified a potent partial agonist that selectively engages a G protein subtype. We further investigated the differences in G protein engagement at 5-HT1A with cryo-electron microscopy, determining structures of 5-HT1A bound to distinct ligands and G protein subtypes. Combined with subsequent structure-guided mutagenesis and signaling assays, our studies uncover both orthosteric and allosteric determinants of agonist-specific stimulation of distinct transducers. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9dyf.cif.gz 9dyf.cif.gz | 189.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9dyf.ent.gz pdb9dyf.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9dyf.json.gz 9dyf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9dyf_validation.pdf.gz 9dyf_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9dyf_full_validation.pdf.gz 9dyf_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9dyf_validation.xml.gz 9dyf_validation.xml.gz | 36 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9dyf_validation.cif.gz 9dyf_validation.cif.gz | 53.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dy/9dyf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dy/9dyf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dy/9dyf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dy/9dyf | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  47302MC  9dydC  9dyeC  9md1C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Guanine nucleotide-binding protein ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABG
| #1: Protein | Mass: 40414.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAI1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAI1 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 39418.086 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 7861.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules R
| #4: Protein | Mass: 61375.930 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: residues 1-25 of the 5-HT receptor deleted / Mutation: L125W Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: cybC, HTR1A, ADRB2RL1, ADRBRL1 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 5 molecules 
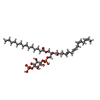

| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-A1BIR / ( Mass: 285.768 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C17H16ClNO / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #6: Chemical | | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-J40 / [( | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Sample was mono disperse following gel filtration. The sample was immediately concentrated for CryoEM grid preparation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: Blot force 3 for 3-5 seconds was used and subsequent grids were screened for ice thickness prior to data collection. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64.03 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 4197 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 8183793 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.74 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 666873 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj


































