[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
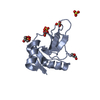
Yorodumi- PDB-9dkz: In situ microED structure of the Eosinophil major basic protein-1 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9dkz | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | In situ microED structure of the Eosinophil major basic protein-1 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Bone marrow proteoglycan | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Effector / Nanocrystal / In-situ / Intracellular | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationextracellular matrix structural constituent conferring compression resistance / defense response to nematode / negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production / negative regulation of interleukin-10 production / positive regulation of interleukin-4 production / transport vesicle / heparin binding / : / carbohydrate binding / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen ...extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring compression resistance / defense response to nematode / negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production / negative regulation of interleukin-10 production / positive regulation of interleukin-4 production / transport vesicle / heparin binding / : / carbohydrate binding / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / defense response to bacterium / immune response / Neutrophil degranulation / extracellular exosome / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY / electron crystallography / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yang, J.E. / Bingman, C.A. / Mitchell, J. / Mosher, D. / Wright, E.R. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2024Title: In situ crystalline structure of the human eosinophil major basic protein-1. Authors: Jie E Yang / Joshua M Mitchell / Craig A Bingman / Deane F Mosher / Elizabeth R Wright /  Abstract: Eosinophils are white blood cells that participate in innate immune responses and have an essential role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. Upon activation, eosinophils ...Eosinophils are white blood cells that participate in innate immune responses and have an essential role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. Upon activation, eosinophils release cytotoxic proteins such as major basic protein-1 (MBP-1) from cytoplasmic secretory granules (SGr) wherein MBP-1 is stored as nanocrystals. How the MBP-1 nanocrystalline core is formed, stabilized, and subsequently mobilized remains unknown. Here, we report the structure of crystalline MBP-1 within SGrs of human eosinophils. The structure reveals a mechanism for intragranular crystal packing and stabilization of MBP-1 via a structurally conserved loop region that is associated with calcium-dependent carbohydrate binding in other C-type lectin (CTL) proteins. Single-cell and single-SGr profiling correlating real-space three-dimensional information from cellular montage cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) and microcrystal electron diffraction (MicroED) data obtained from non-activated and IL33-activated eosinophils revealed activation-dependent crystal expansion and extrusion of expanded crystals from SGr. These results suggest that MBP-1 crystals play a dynamic role in the release of SGr contents. Collectively, this research demonstrates the importance of macromolecular structure determination. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9dkz.cif.gz 9dkz.cif.gz | 61 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9dkz.ent.gz pdb9dkz.ent.gz | 41.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9dkz.json.gz 9dkz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9dkz_validation.pdf.gz 9dkz_validation.pdf.gz | 413.8 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9dkz_full_validation.pdf.gz 9dkz_full_validation.pdf.gz | 414 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9dkz_validation.xml.gz 9dkz_validation.xml.gz | 7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9dkz_validation.cif.gz 9dkz_validation.cif.gz | 8.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/9dkz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/9dkz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/9dkz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/9dkz | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 13694.769 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: The major basic protein-1 structure was directly determined from intragranular nanocrystals inside unperturbed human eosinophil cells obtained from donors. Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: blood / Cell: eosinophil / Gene: PRG2, MBP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Tissue: blood / Cell: eosinophil / Gene: PRG2, MBP / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13727 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13727 |
|---|---|
| #2: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: CELL / 3D reconstruction method: electron crystallography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: In situ microED structure of the Eosinophil major basic protein-1 Type: CELL Details: Mature human eosinophil cells were collected and purified from human donor blood. This was followed by eosinophil cell deposition on EM grids, grid plunge-freezing, and cryo-FIB milling of ...Details: Mature human eosinophil cells were collected and purified from human donor blood. This was followed by eosinophil cell deposition on EM grids, grid plunge-freezing, and cryo-FIB milling of individual eosinophil cells. Cryo-FIB milling of the cells exposed unperturbed cytosolic secretory granules, inside which nanocrystals of the major basic protein-1 were located. Micro-ED data was collected on these crystals for in-situ structure determination. Entity ID: #1 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: cytoplasm / Organelle: mature eosinophil secretory granule / Tissue: blood Homo sapiens (human) / Cellular location: cytoplasm / Organelle: mature eosinophil secretory granule / Tissue: blood |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 / Details: secretory granule matrix |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1000000 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Human eosinophil cells were collected from human donor blood. The cells were rested in 1640 RPMI medium supplemented with 0.1% human serum albumin, before direct deposition onto gold EM ...Details: Human eosinophil cells were collected from human donor blood. The cells were rested in 1640 RPMI medium supplemented with 0.1% human serum albumin, before direct deposition onto gold EM grids and plunge freezing. Subsequently, cryo-FIB milling was used to expose unperturbed intragranular major basic protien-1 nanocrystals present within the cytosolic secretory granules. |
| Specimen support | Details: 10 mA / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil |
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 310.15 K / Details: Blot time of 6~8 sec, single-side back blotting |
-Data collection
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 0 nm / Nominal defocus min: 0 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 0 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 0 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 100 K / Temperature (min): 85 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1 sec. / Electron dose: 0.15 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI CETA (4k x 4k) / Num. of diffraction images: 40 / Num. of grids imaged: 3 Details: The final dataset was merged from six crystals, each with 40 images. Tilt was -20 to +20 degrees, 1 degree per frame, 1 second per frame | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM diffraction shell | Resolution: 3.2→28.93 Å / Fourier space coverage: 95.6 % / Multiplicity: 7.5 / Num. of structure factors: 1912 / Phase residual: 26.33 ° | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM diffraction stats | Fourier space coverage: 95.6 % / High resolution: 3.2 Å / Num. of intensities measured: 24722 / Num. of structure factors: 3303 / Phase error: 26.33 ° / Phase error rejection criteria: 0 / Rmerge: 67.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Highest resolution: 3.2 Å / Num. obs: 1912 / % possible obs: 96.1 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 85.01 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.931 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.69 / Rrim(I) all: 0.719 / Net I/σ(I): 3.2 / Num. measured all: 24817 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM 3D crystal entity | ∠α: 90 ° / ∠β: 90 ° / ∠γ: 90 ° / A: 31.24 Å / B: 57.87 Å / C: 59.06 Å / Space group name: P22121 / Space group num: 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: DIFFRACTION PATTERN/LAYERLINES / Symmetry type: 3D CRYSTAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: RECIPROCAL Details: Alternating rounds of phenix.refine and map filling in Coot | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Chain-ID: A / Chain residue range: 106-222
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 3.2→28.93 Å / SU ML: 0.2682 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / Phase error: 26.171 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.1 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 91.79 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj