[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
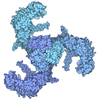
Yorodumi- PDB-9cuj: Structure of human full-length derived TRPV6 channel in apo open state -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9cuj | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human full-length derived TRPV6 channel in apo open state | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / transient receptor potential V family member 6 / TRP / channel / TRPV6 / TRP channels / derived | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationparathyroid hormone secretion / regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis / TRP channels / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / calcium ion homeostasis / calcium channel complex / response to calcium ion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel activity / calcium ion transport ...parathyroid hormone secretion / regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis / TRP channels / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / calcium ion homeostasis / calcium channel complex / response to calcium ion / calcium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel activity / calcium ion transport / calmodulin binding / metal ion binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.78 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Neuberger, A. / Nadezhdin, K.D. / Sobolevsky, A.I. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Germany, 5items Germany, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2025 Journal: Structure / Year: 2025Title: Structure-function analyses of human TRPV6 ancestral and derived haplotypes. Authors: Arthur Neuberger / Alexey Shalygin / Yury A Trofimov / Irina I Veretenenko / Kirill D Nadezhdin / Nikolay A Krylov / Thomas Gudermann / Roman G Efremov / Vladimir Chubanov / Alexander I Sobolevsky /    Abstract: TRPV6 is a Ca selective channel that mediates calcium uptake in the gut and contributes to the development and progression of human cancers. TRPV6 is represented by the ancestral and derived ...TRPV6 is a Ca selective channel that mediates calcium uptake in the gut and contributes to the development and progression of human cancers. TRPV6 is represented by the ancestral and derived haplotypes that differ by three non-synonymous polymorphisms, located in the N-terminal ankyrin repeat domain (C157R), S1-S2 extracellular loop (M378V), and C-terminus (M681T). The ancestral and derived haplotypes were proposed to serve as genomic factors causing a different outcome for cancer patients of African ancestry. We solved cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of ancestral and derived TRPV6 in the open and calmodulin (CaM)-bound inactivated states. Neither state shows substantial structural differences caused by the non-synonymous polymorphisms. Functional properties assessed by electrophysiological recordings and Ca uptake measurements, and water and ion permeation evaluated by molecular modeling also appear similar between the haplotypes. Therefore, ancestral and derived TRPV6 have similar structure and function, implying that other factors are responsible for the differences in susceptibility to cancer. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9cuj.cif.gz 9cuj.cif.gz | 487 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9cuj.ent.gz pdb9cuj.ent.gz | 397.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9cuj.json.gz 9cuj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cu/9cuj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cu/9cuj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cu/9cuj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cu/9cuj | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  45935MC  9cuhC  9cuiC  9cukC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 87383.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRPV6, ECAC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TRPV6, ECAC2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H1D0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H1D0 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 137 molecules 








| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-Y01 / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( #4: Chemical | ChemComp-PCW / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / | #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: derived hTRPV6 tetramer in open apo state / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.37 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Human embryonic kidney 293 / Plasmid: pEG BacMam Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Human embryonic kidney 293 / Plasmid: pEG BacMam | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.9 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: human TRPV6 in cNW11 nanodiscs | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.5 sec. / Electron dose: 58 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 12516 |
| Image scans | Width: 11520 / Height: 8184 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18 / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 9029804 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.78 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 554157 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj