[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9ccr: Crystal structure of the EspE7 thioesterase mutant R35A from the ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9ccr | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
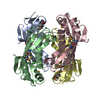
| Title | Crystal structure of the EspE7 thioesterase mutant R35A from the esperamicin biosynthetic pathway at 1.6 A | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Thioesterase | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / thioesterase / hot-dog / enediyne biosynthetic pathway / esperamicin biosynthesis / Natural product biosynthesis | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology | Thioesterase-like superfamily / HotDog domain superfamily / DODECYL-COA / : / Thioesterase Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Actinomadura verrucosospora (bacteria) Actinomadura verrucosospora (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.57 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.57 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Miller, M.D. / Hankore, E.D. / Xu, W. / Kosgei, A.J. / Bhardwaj, M. / Thorson, J.S. / Van Lanen, S.G. / Phillips Jr., G.N. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J.Nat.Prod. / Year: 2025 Journal: J.Nat.Prod. / Year: 2025Title: Functional and Structural Studies on the Esperamicin Thioesterase and Progress toward Understanding Enediyne Core Biosynthesis. Authors: Hankore, E.D. / Miller, M.D. / Kosgei, A.J. / Xu, W. / Tan, K. / Endres, M. / Bhardwaj, M. / Joachimiak, G. / Joachimiak, A. / Phillips Jr., G.N. / Thorson, J.S. / Van Lanen, S.G. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9ccr.cif.gz 9ccr.cif.gz | 433 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9ccr.ent.gz pdb9ccr.ent.gz | 296.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9ccr.json.gz 9ccr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/9ccr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/9ccr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/9ccr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cc/9ccr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 20232.805 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mutation: E35A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: codon optimized synthetic gene / Source: (gene. exp.)  Actinomadura verrucosospora (bacteria) / Gene: EspE7 / Plasmid: EspE7_pCDFDuet / Production host: Actinomadura verrucosospora (bacteria) / Gene: EspE7 / Plasmid: EspE7_pCDFDuet / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-DCC / #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 1.96 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 37.38 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 8 Details: 30% glycerol, 1.5 M sodium chloride, 5 mM Tris, pH 8, and 3 % ethanol, Additive: 0.2 M non-detergent sulfobetaine (NDSB-201) |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 23-ID-B / Wavelength: 1.03317 Å / Beamline: 23-ID-B / Wavelength: 1.03317 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jul 16, 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.03317 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.57→65.59 Å / Num. obs: 88647 / % possible obs: 98.9 % / Redundancy: 6.8 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 29.14 Å2 Data reduction details: Data were integrated, scaled and merged with the Dials software package using the xia2 pipeline CC1/2: 0.999 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.06 / Rpim(I) all: 0.024 / Rrim(I) all: 0.065 / Net I/σ(I): 12.1 / Num. measured all: 601685 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.57→65.59 Å / SU ML: 0.2779 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 25.2272 MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.57→65.59 Å / SU ML: 0.2779 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 25.2272 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 Details: 1. Hydrogen atoms have been modeled in their riding positions. 2. Mass spectrometry of purified protein shows that Palmitoyl-CoA copurifies with the EspE7-R35A protein during purification ...Details: 1. Hydrogen atoms have been modeled in their riding positions. 2. Mass spectrometry of purified protein shows that Palmitoyl-CoA copurifies with the EspE7-R35A protein during purification when expressed in E.coli. The CoA adduct seen in the electron density maps is disordered to varying degrees in the different pockets in the asymmetric unit. In one pocket, most of the Palmitoyl-CoA can be built with the Adenosine positioned in a less common position relative to other homologs with CoA adducts bound. This is likely due to packing constraints. In some symmetry copies, there is considerable disorder of the region beyond the diphosphate and the Adenosine was left unmodeled with some difference peaks that likely represent its multiple positions. Along the fatty acid chain, the density gets weaker as one goes further from the CoA and deeper into the binding pocket. Most chains have good density to around the C8-C10 position with not much density beyond C12. Building full length Palmitoyl tail in the pocket results in negative difference density for the terminal atoms. There is also clear disorder for the side-chain of Met-91 with one conformer blocking longer chain fatty acids in the pocket. In the end, the ligand was modeled as dodecyl-CoA (lauryl-CoA). The presumption is that there could be a mix of fatty acid chain lengths of coA adducts bound and co-purified. 3. The metal ion near the fatty acid chain was modeled as a potassium ion. The presence of an anomalous peak similar in height to sulfur atoms suggests it is heavier than Na or Mg. The height of this anomalous peak is unchanged when the data was re-collected above and below the Zn K-edge and below the iron K-edge, suggesting that the metal must be lighter than Fe. The lack of a signal for Mn in an X-ray fluorescence emission spectra suggests it is not Mn. The two most likely candidates from the anomalous and X-ray fluorescence experiments is Calcium and Potassium - both of which would have anomalous peaks at the energies used for data collection (12000, 9709, 9609 and 7000 eV) and also emit at an energy below where the beamline setup can detect in the emission spectra. Looking at the results of the geometric and valence sum criteria when modeled as Ca and K on the check my metal server, both options had several criteria that were supportive of the assignment and some that were marginal. In the end, K was selected as being slightly more favorable but the assignment is not definitive. 4. There are a large number of residues at the N- and C-termini that cannot be built due to disorder. The C-terminal region was predicted to be disordered. An extra 10 residues from chain B can be built as they are packed against a symmetry adjacent tetramer. In chain D, density for the C-terminus packing against a neighboring tetramer is also visible, but it is not ordered enough to reliably build. The N-terminal expression and purification tag cannot be built. There are a number of un-built difference map peaks along the surface of the protein that are likely protein residues from the C-terminus or N-terminus of symmetry adjacent tetramers, but it was not possible to build and identify the register of these residues.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.1 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 40.9 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.57→65.59 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj