[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
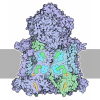
Yorodumi- PDB-9c12: Leukotriene C4-bound Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2 (MRP2) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9c12 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Leukotriene C4-bound Multidrug Resistance-associated Protein 2 (MRP2) | ||||||
 Components Components | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / ABC transporter / Multidrug resistance / Substrate | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDefective ABCC2 causes DJS / bilirubin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic export from cell / leukotriene transport / ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity / ABC-type glutathione-S-conjugate transporter / : / heme catabolic process / Atorvastatin ADME / xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier ...Defective ABCC2 causes DJS / bilirubin transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic export from cell / leukotriene transport / ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity / ABC-type glutathione-S-conjugate transporter / : / heme catabolic process / Atorvastatin ADME / xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier / bilirubin transport / xenobiotic transmembrane transport / intercellular canaliculus / : / transepithelial transport / Paracetamol ADME / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter / Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of other compounds; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity / Heme degradation / bile acid and bile salt transport / Aspirin ADME / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type transporter activity / transport across blood-brain barrier / xenobiotic metabolic process / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / transmembrane transport / apical plasma membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / cell surface / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.75 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Koide, E. / Chen, J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis for the transport and regulation mechanism of the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2. Authors: Eriko Koide / Harlan L Pietz / Jean Beltran / Jue Chen /  Abstract: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) is an ATP-powered exporter important for maintaining liver homeostasis and a potential contributor to chemotherapeutic resistance. Using cryogenic ...Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) is an ATP-powered exporter important for maintaining liver homeostasis and a potential contributor to chemotherapeutic resistance. Using cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we determine the structures of human MRP2 in three conformational states: an autoinhibited state, a substrate-bound pre-translocation state, and an ATP-bound post-translocation state. In the autoinhibited state, the cytosolic regulatory (R) domain plugs into the transmembrane substrate-binding site and extends into the cytosol to form a composite ATP-binding site at the surface of nucleotide-binding domain 2. Substrate displaces the R domain, permitting conformational changes necessary for transport. These observations suggest that the R domain functions as a selectivity gauge, where only at sufficiently high concentrations can the substrate effectively initiate transport. Comparative structural analyzes of MRP2 bound to various substrates, as determined in this study and others, reveal how MRP2 recognizes a diverse array of compounds, supporting its role in multidrug resistance. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Title: Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty ...Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert D Oeffner / Billy K Poon / Michael G Prisant / Randy J Read / Jane S Richardson / David C Richardson / Massimo D Sammito / Oleg V Sobolev / Duncan H Stockwell / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre G Urzhumtsev / Lizbeth L Videau / Christopher J Williams / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological ...Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological processes and to develop new therapeutics against diseases. The overall structure-solution workflow is similar for these techniques, but nuances exist because the properties of the reduced experimental data are different. Software tools for structure determination should therefore be tailored for each method. Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination that handles data from any of these techniques. Tasks performed with Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle and deposition. Each tool caters to the type of experimental data. The design of Phenix emphasizes the automation of procedures, where possible, to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default parameters are chosen to encourage best practice. A graphical user interface provides access to many command-line features of Phenix and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking and re-running of previous tasks. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9c12.cif.gz 9c12.cif.gz | 289.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9c12.ent.gz pdb9c12.ent.gz | 225.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9c12.json.gz 9c12.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/9c12 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/9c12 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/9c12 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/9c12 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  45099MC  9br2C  9bukC  9c2iC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 174392.344 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ABCC2, CMOAT, CMOAT1, CMRP, MRP2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ABCC2, CMOAT, CMOAT1, CMRP, MRP2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: Q92887, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of other compounds; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate, ABC-type xenobiotic transporter, ABC-type ...References: UniProt: Q92887, Translocases; Catalysing the translocation of other compounds; Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate, ABC-type xenobiotic transporter, ABC-type glutathione-S-conjugate transporter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
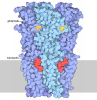
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-LTX / ( | ||||||
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CLR / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-UNL / Mass: 790.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 13 / Source method: obtained synthetically Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: wild type MRP2 bound to its substrate, leukotriene C4 / Type: CELL / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: Digitonin is solubilized overnight. prior to use, it is filtered using a 0.22 uM filter. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: single-particle MRP2 in digitonin micelle. Mixed with 285 uM LTC4. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R0.6/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 65 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21.1_5286 / Category: model refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.75 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 83725 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj