[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
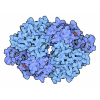
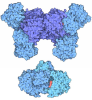
Yorodumi- PDB-9b5i: Ubiquitin E1-Ub-E2 tetrahedral transthiolation intermediate mimic... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9b5i | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Ubiquitin E1-Ub-E2 tetrahedral transthiolation intermediate mimic (doubly Ub-loaded) - cluster 4 map and model (Ub(A)-AMP/PPi/Mg) | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / UBIQUITIN / E1 / E2 / UBA1 / UBC4 / TRANSTHIOESTERIFICATION / THIOESTER / TRANSTHIOLATION / TETRAHEDRAL INTERMEDIATE / ADENYLATION / INHIBITOR / NUCLEUS / PHOSPHOPROTEIN / UBL CONJUGATION PATHWAY / UBL / ATP ATP-BINDING / AMP / NUCLEOTIDE-BINDING / ISOPEPTIDE BOND | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / Josephin domain DUBs / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Interleukin-1 signaling / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / RAS processing / Pexophagy / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism ...PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Regulation of necroptotic cell death / Josephin domain DUBs / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Interleukin-1 signaling / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / RAS processing / Pexophagy / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / Translesion synthesis by POLK / Translesion synthesis by POLI / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / UCH proteinases / Orc1 removal from chromatin / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Ubiquitin Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Aggrephagy / Ub-specific processing proteases / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Neddylation / Metalloprotease DUBs / Regulation of PTEN localization / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, meiosis-specific transcripts / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Peroxisomal protein import / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / nuclear SCF ubiquitin ligase complex / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme / ubiquitin activating enzyme activity / SREBP signaling pathway / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / enzyme inhibitor activity / SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / ubiquitin ligase complex / meiotic cell cycle / modification-dependent protein catabolic process / protein polyubiquitination / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / protein tag activity / ribosome biogenesis / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasmic translation / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / protein ubiquitination / structural constituent of ribosome / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kochanczyk, T. / Lima, C.D. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for transthiolation intermediates in the ubiquitin pathway. Authors: Tomasz Kochańczyk / Zachary S Hann / Michaelyn C Lux / Avelyn Mae V Delos Reyes / Cheng Ji / Derek S Tan / Christopher D Lima /  Abstract: Transthiolation (also known as transthioesterification) reactions are used in the biosynthesis of acetyl coenzyme A, fatty acids and polyketides, and for post-translational modification by ubiquitin ...Transthiolation (also known as transthioesterification) reactions are used in the biosynthesis of acetyl coenzyme A, fatty acids and polyketides, and for post-translational modification by ubiquitin (Ub) and ubiquitin-like (Ubl) proteins. For the Ub pathway, E1 enzymes catalyse transthiolation from an E1~Ub thioester to an E2~Ub thioester. Transthiolation is also required for transfer of Ub from an E2~Ub thioester to HECT (homologous to E6AP C terminus) and RBR (ring-between-ring) E3 ligases to form E3~Ub thioesters. How isoenergetic transfer of thioester bonds is driven forward by enzymes in the Ub pathway remains unclear. Here we isolate mimics of transient transthiolation intermediates for E1-Ub(T)-E2 and E2-Ub(T)-E3 complexes (where T denotes Ub in a thioester or Ub undergoing transthiolation) using a chemical strategy with native enzymes and near-native Ub to capture and visualize a continuum of structures determined by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. These structures and accompanying biochemical experiments illuminate conformational changes in Ub, E1, E2 and E3 that are coordinated with the chemical reactions to facilitate directional transfer of Ub from each enzyme to the next. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9b5i.cif.gz 9b5i.cif.gz | 256.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9b5i.ent.gz pdb9b5i.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9b5i.json.gz 9b5i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  9b5i_validation.pdf.gz 9b5i_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  9b5i_full_validation.pdf.gz 9b5i_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  9b5i_validation.xml.gz 9b5i_validation.xml.gz | 49.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  9b5i_validation.cif.gz 9b5i_validation.cif.gz | 73.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/9b5i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/9b5i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/9b5i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b5/9b5i | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44213MC  9b55C  9b56C  9b57C  9b58C  9b59C  9b5aC  9b5bC  9b5cC  9b5dC  9b5eC  9b5fC  9b5gC  9b5hC  9b5jC  9b5kC  9b5lC  9b5mC  9b5nC  9b5oC  9b5pC  9b5qC  9b5rC  9b5sC  9b5tC  9b5uC  9b5vC  9b5wC  9b5xC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 111764.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: residues 13-1012 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: ptr3, SPBC1604.21c, SPBC211.09 / Plasmid: pSMT3 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 8568.769 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: ubi4, SPBC337.08c / Plasmid: pET3C / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 17043.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C21S,C107S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: ubc4, SPBC119.02 / Plasmid: pET29b+ / Production host:  References: UniProt: P46595, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 8769.948 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: 972 / ATCC 24843 / Gene: uep1, ubi2, SPAC1805.12c / Plasmid: pTXB1 / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 5 molecules 
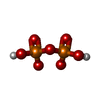
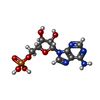


| #5: Chemical | | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-POP / | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-AMP / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-A1AIV / | Mass: 84.120 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C4H8N2 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Covalent E1-Ub-E2 transthiolation intermediate mimic complex with second Ub bound to E1 (doubly Ub-loaded E1-Ub-E2 complex) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.2 Details: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ATP, 0.05% CHAPSO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4 sec. / Electron dose: 72 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 324446 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 PDBj
PDBj