+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8y3e | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the overlapping di-nucleosome (open form) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION/DNA / chromatin / GENE REGULATION / GENE REGULATION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere ...negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / killing of cells of another organism / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / cadherin binding / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.32 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Tanaka, H. / Nishimura, M. / Takizawa, Y. / Nozawa, K. / Ehara, H. / Sekine, S. / Kurumizaka, H. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 4items Japan, 4items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PNAS Nexus / Year: 2024 Journal: PNAS Nexus / Year: 2024Title: Asymmetric fluctuation of overlapping dinucleosome studied by cryoelectron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering. Authors: Masahiro Shimizu / Hiroki Tanaka / Masahiro Nishimura / Nobuhiro Sato / Kayo Nozawa / Haruhiko Ehara / Shun-Ichi Sekine / Ken Morishima / Rintaro Inoue / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Hitoshi ...Authors: Masahiro Shimizu / Hiroki Tanaka / Masahiro Nishimura / Nobuhiro Sato / Kayo Nozawa / Haruhiko Ehara / Shun-Ichi Sekine / Ken Morishima / Rintaro Inoue / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Hitoshi Kurumizaka / Masaaki Sugiyama /  Abstract: Nucleosome remodelers modify the local structure of chromatin to release the region from nucleosome-mediated transcriptional suppression. Overlapping dinucleosomes (OLDNs) are nucleoprotein complexes ...Nucleosome remodelers modify the local structure of chromatin to release the region from nucleosome-mediated transcriptional suppression. Overlapping dinucleosomes (OLDNs) are nucleoprotein complexes formed around transcription start sites as a result of remodeling, and they consist of two nucleosome moieties: a histone octamer wrapped by DNA (octasome) and a histone hexamer wrapped by DNA (hexasome). While OLDN formation alters chromatin accessibility to proteins, the structural mechanism behind this process is poorly understood. Thus, this study investigated the characteristics of structural fluctuations in OLDNs. First, multiple structures of the OLDN were visualized through cryoelectron microscopy (cryoEM), providing an overview of the tilting motion of the hexasome relative to the octasome at the near-atomistic resolution. Second, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) revealed the presence of OLDN conformations with a larger radius of gyration than cryoEM structures. A more complete description of OLDN fluctuation was proposed by SAXS-based ensemble modeling, which included possible transient structures. The ensemble model supported the tilting motion of the OLDN outlined by the cryoEM models, further suggesting the presence of more diverse conformations. The amplitude of the relative tilting motion of the hexasome was larger, and the nanoscale fluctuation in distance between the octasome and hexasome was also proposed. The cryoEM models were found to be mapped in the energetically stable region of the conformational distribution of the ensemble. Exhaustive complex modeling using all conformations that appeared in the structural ensemble suggested that conformational and motional asymmetries of the OLDN result in asymmetries in the accessibility of OLDN-binding proteins. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8y3e.cif.gz 8y3e.cif.gz | 466.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8y3e.ent.gz pdb8y3e.ent.gz | 354.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8y3e.json.gz 8y3e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y3/8y3e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y3/8y3e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y3/8y3e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y3/8y3e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  38879MC  8y3cC  8y3dC  8y3fC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 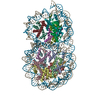
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 14 molecules AEKOBFLPCGMDHN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15719.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11676.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14447.825 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC4, H2AFM, HIST1H2AB, H2AC8, H2AFA, HIST1H2AE / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 14217.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC11, H2BFR, HIST1H2BJ / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC11, H2BFR, HIST1H2BJ / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 77664.383 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 76734.789 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Overlapping di-nucleosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 650 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.32 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 133196 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj










































