[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8wci: Cryo-EM structure of the inhibitor-bound Vo complex from Enteroco... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8wci | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
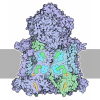
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the inhibitor-bound Vo complex from Enterococcus hirae | |||||||||
 Components Components | (V-type sodium ATPase subunit ...) x 2 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE/HYDROLASE INHIBITOR / V-ATPase / Na+-transporting / membrane protein / ATP hydrolyses / HYDROLASE / HYDROLASE-HYDROLASE INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / sodium ion transport / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / ATPase binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Suzuki, K. / Mikuriya, S. / Adachi, N. / Kawasaki, M. / Senda, T. / Moriya, T. / Murata, T. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 2items Japan, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Na-V-ATPase inhibitor curbs VRE growth and unveils Na pathway structure. Authors: Kano Suzuki / Yoshiyuki Goto / Akihiro Otomo / Kouki Shimizu / Shohei Abe / Katsuhiko Moriyama / Satoshi Yasuda / Yusuke Hashimoto / Jun Kurushima / Sho Mikuriya / Fabiana L Imai / Naruhiko ...Authors: Kano Suzuki / Yoshiyuki Goto / Akihiro Otomo / Kouki Shimizu / Shohei Abe / Katsuhiko Moriyama / Satoshi Yasuda / Yusuke Hashimoto / Jun Kurushima / Sho Mikuriya / Fabiana L Imai / Naruhiko Adachi / Masato Kawasaki / Yumi Sato / Satoshi Ogasawara / So Iwata / Toshiya Senda / Mitsunori Ikeguchi / Haruyoshi Tomita / Ryota Iino / Toshio Moriya / Takeshi Murata /  Abstract: Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE) is a major cause of nosocomial infections, particularly endocarditis and sepsis. With the diminishing effectiveness of antibiotics against VRE, new ...Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE) is a major cause of nosocomial infections, particularly endocarditis and sepsis. With the diminishing effectiveness of antibiotics against VRE, new antimicrobial agents are urgently needed. Our previous research demonstrated the crucial role of Na-transporting V-ATPase in Enterococcus hirae for growth under alkaline conditions. In this study, we identified a compound, V-161, from 70,600 compounds, which markedly inhibits E. hirae V-ATPase activity. V-161 not only inhibits VRE growth in alkaline conditions but also significantly suppresses VRE colonization in the mouse small intestine. Furthermore, we unveiled the high-resolution structure of the membrane V part due to V-161 binding. V-161 binds to the interface of the c-ring and a-subunit, constituting the Na transport pathway in the membrane, thereby halting its rotation. This structural insight presents potential avenues for developing therapeutic agents for VRE treatment and elucidates the Na transport pathway and mechanism. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8wci.cif.gz 8wci.cif.gz | 348 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8wci.ent.gz pdb8wci.ent.gz | 275.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8wci.json.gz 8wci.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wc/8wci https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wc/8wci ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wc/8wci ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wc/8wci | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37440MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type sodium ATPase subunit ... , 2 types, 11 molecules ABCDEFGHIJP
| #1: Protein | Mass: 16043.918 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria)Gene: ntpK, ntpN, EHR_08240 / Production host:  #2: Protein | | Mass: 76515.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria)Gene: ntpI / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 239 molecules 




| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CDL / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-NA / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-W3K / | Mass: 251.326 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C16H17N3 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: V-ATPase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.735 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) Enterococcus hirae ATCC 9790 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 49 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 15 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1008654 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 225359 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 32.58 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj