[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8uxu: Cryo-EM structure of a bacterial nitrilase filament with a covale... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8uxu | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
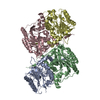
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a bacterial nitrilase filament with a covalent adduct derived from benzonitrile hydrolysis | ||||||
 Components Components | Nitrilase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Aromatic-nitrilase / helical-filament / benzaldehyde covalent-adduct intermediate / truncated mutant | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Rhodococcus sp. (bacteria) Rhodococcus sp. (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.01 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Aguirre-Sampieri, S. / Casanal, A. / Emsley, P. / Garza-Ramos, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Mexico, 1items Mexico, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structure of bacterial nitrilase reveals insight into oligomerization, substrate recognition, and catalysis. Authors: Sergio Aguirre-Sampieri / Ana Casañal / Paul Emsley / Georgina Garza-Ramos /    Abstract: Many enzymes can self-assemble into higher-order structures with helical symmetry. A particularly noteworthy example is that of nitrilases, enzymes in which oligomerization of dimers into spiral homo- ...Many enzymes can self-assemble into higher-order structures with helical symmetry. A particularly noteworthy example is that of nitrilases, enzymes in which oligomerization of dimers into spiral homo-oligomers is a requirement for their enzymatic function. Nitrilases are widespread in nature where they catalyze the hydrolysis of nitriles into the corresponding carboxylic acid and ammonia. Here, we present the Cryo-EM structure, at 3 Å resolution, of a C-terminal truncate nitrilase from Rhodococcus sp. V51B that assembles in helical filaments. The model comprises a complete turn of the helical arrangement with a substrate-intermediate bound to the catalytic cysteine. The structure was solved having added the substrate to the protein. The length and stability of filaments was made more substantial in the presence of the aromatic substrate, benzonitrile, but not for aliphatic nitriles or dinitriles. The overall structure maintains the topology of the nitrilase family, and the filament is formed by the association of dimers in a chain-like mechanism that stabilizes the spiral. The active site is completely buried inside each monomer, while the substrate binding pocket was observed within the oligomerization interfaces. The present structure is in a closed configuration, judging by the position of the lid, suggesting that the intermediate is one of the covalent adducts. The proximity of the active site to the dimerization and oligomerization interfaces, allows the dimer to sense structural changes once the benzonitrile was bound, and translated to the rest of the filament, stabilizing the helical structure. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8uxu.cif.gz 8uxu.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8uxu.ent.gz pdb8uxu.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8uxu.json.gz 8uxu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ux/8uxu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  42779MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 36254.840 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 / Fragment: C-terminal truncated mutant Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Rhodococcus sp. (in: high G+C Gram-positive bacteria) (bacteria) Rhodococcus sp. (in: high G+C Gram-positive bacteria) (bacteria)Strain: V51B / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-HBX / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Bacterial nitrilase filament with covalent adduct derived from benzonitrile hydrolysis. Type: COMPLEX / Details: C-terminal truncated mutant. / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Rhodococcus sp. (in: high G+C Gram-positive bacteria) (bacteria) Rhodococcus sp. (in: high G+C Gram-positive bacteria) (bacteria)Strain: V51B | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 Details: Monobasic and dibasic potassium phosphate mixed at 7.8 pH. | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 3.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Purified protein was centrifuged and incubated with 100 mM benzonitrile for 15 min and applied to the grid. | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K Details: Grids were glow-discharged for 60 sec before deposition of 3 ul sample, blotted for 4 s, and vitrified by plunging into liquid ethane and stored in a cryobox in liquid nitrogen. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Nominal defocus max: 5000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.04081633 sec. / Electron dose: 1 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 2358 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 140381 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.01 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 56369 / Num. of class averages: 45 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 37.82 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj